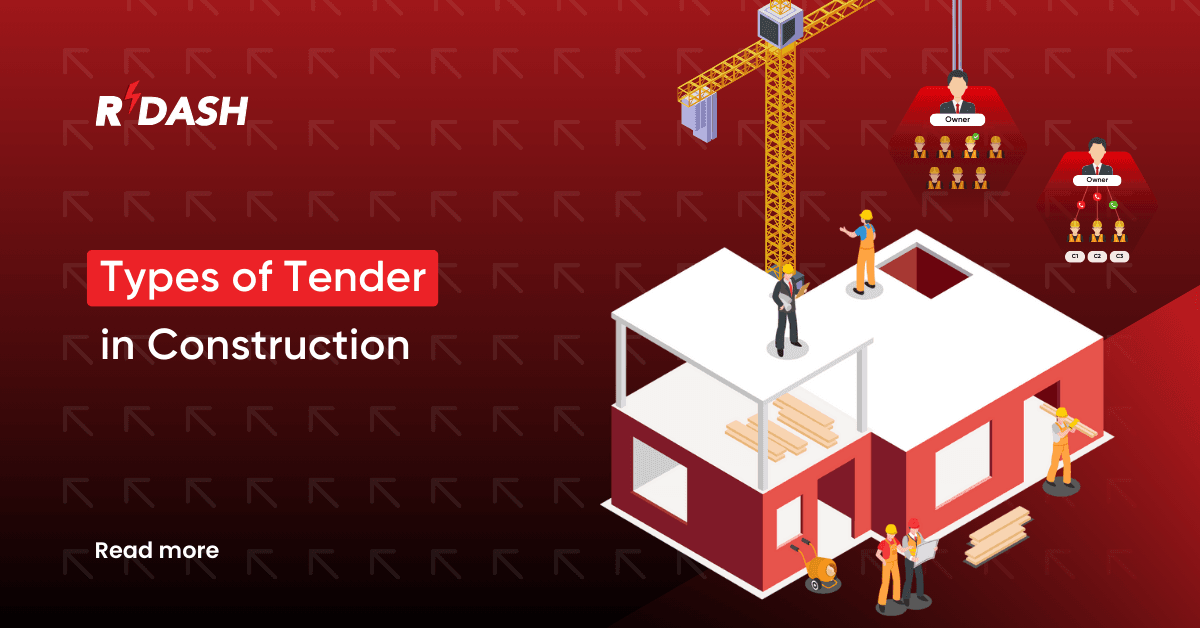
Tendering is the backbone of the construction procurement process that allows clients to pick a contractor who can deliver a project efficiently, cost-effectively, and with quality. The choice of tendering depends on the scope, complexity, and specific needs of a project.
Types of tender in construction
The most widely used types of tender include open tendering, selective tendering, and negotiated tendering. Each has unique characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages that impact the outcome of the project.
Open Tendering
Open tenders refer to inviting all the qualified contractors to submit their bids for a project. The method is mainly followed in public sector projects because of openness and fairness of the process. Most open tenders usually appear as advertised in public notice so that interested parties have equal opportunities to participate.
Benefits:
Competitive Pricing
Open tendering encourages competition as many contractors can participate, thus encouraging more competitive bids. This often leads to competitive pricing, which in turn saves costs for the client.
Transparency
The process is highly transparent since all contractors are accorded equal access to project information and bidding opportunities. Openness creates trust and ensures accountability.
Opportunities for All
Open tendering gives equal chances to the small, medium, and large contractors, so less encouragement of broader participation with diversifications in the marketplace.
Fair Selection Process
The criteria for contractor evaluation include cost, technical capability, and compliance with project specifications. This means that the selection process is transparent and merit-based.
Drawbacks:
Time-Consuming
This process involves lengthy periods of advertising, submission of bids, and evaluating them. It can delay the project timeline because decision-making is delayed.
Risk of low-quality bids
The emphasis on cost in competitive bidding can lead to contractors underpricing their bids, which may result in subpar work or hidden costs during execution.
High administrative burden
Managing an open tendering process involves substantial documentation, correspondence, and evaluation, increasing the workload for the client.
Opportunity for Incompetent Contractors
It is also linked with the risk of getting contracts from contractors who do not have relevant experience, skills, and means.
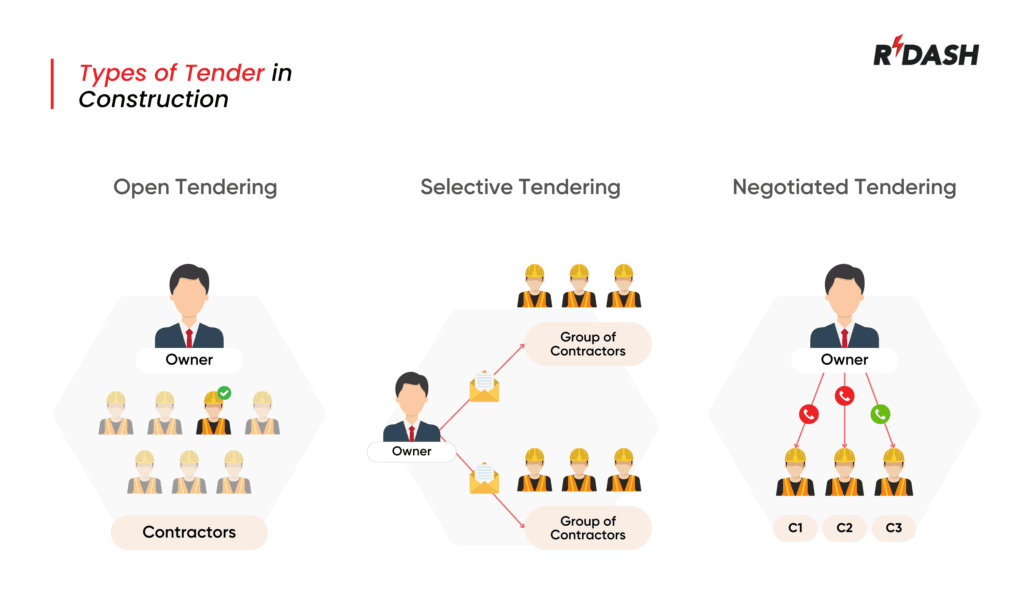
Selective tendering
Selective tendering is the process whereby some contractors are prequalified based on the experience, expertise, and financial capacity for a given project. The process is typically employed in more complex and special projects whereby quality and capabilities are so crucial.
Advantage:
Quality Assurance
Prequalification can also ensure to clients that the firms that will take part in the bidding process are capable and experienced, thereby reducing the likelihood of project delays and resultant quality issues.
Efficiency in bidding
Streamlining results in a smaller pool of bidders, thus saving much time and effort required in the process of evaluation and making decisions.
Focused Competition
Their bids are more accurate and closer to the actual needs of the project because contractors with adequate experience compete with each other.
Reduced risk of low-quality work
Prequalification eliminates contractors who would eventually underdeliver on the project hence ensuring that the project is delivered to a high standard.
Disadvantages:
Limited Competition
It could, therefore, limit the pool of bidders, which might reduce competitive pressure and thus cost higher than open tendering.
Exclusion of Emerging Firms
This might exclude new or small firms as it focuses on past experience and established credentials, which can limit the scope of opportunities for market growth.
Transparency Concerns
This method often appears selective, whereby prequalification criteria must specify what will be a selection process that ensures favoritism and lack of fairness are not employed.
Prequalification Costs
Prequalification may also cost more in terms of time and resources while increasing the cost for procurement.
Selecting the Best Tendering Strategy
It depends on the purpose, complexity, and priorities of the project: open tendering is to be applied when the project has broader concerns- openness, maximum competition, and comprehensiveness in terms of giving the award of public infrastructure works.
On the other hand, selective tendering is well applied to specialized projects wherein there is a need to secure quality, mastery, and efficiency in performing such jobs.
It is just another layer of flexibility and collaboration, so the preferred choice for projects requiring bespoke solutions, fast-track times, or even complex needs that can benefit from early contractor involvement. Especially ideal if the client has a past experience with the contractor and aims to closely align to project objectives.
Negotiated Tendering
Negotiated tendering is the type of procurement where a client negotiates directly with the selected contractors to determine the terms and conditions of the project. This form of procurement is particularly used in highly specialized projects, design-build contracts, and other projects for which the client has a known relationship of trust with the contractor.
Advantages of Negotiated Tendering
Quicker Decision-Making
Negotiated tendering avoids the lengthy processes of advertising, prequalification, and competitive bidding. This makes the negotiated process more time-effective, especially for emergency programs.
Custom Solutions
Since the client works closely with the contractor in negotiating, specific needs and preferences can thereby be met to the scope, design, and execution of the project.
Improved Collaboration
Negotiated tendering promotes fruitful collaboration between the client and contractor, with increased communication and alignment in the lifecycle of the project.
Cost Control
Early contractor involvement can deliver actual cost estimates and value engineering; thereby, assisting clients in making their budget effective.
Reliability and Trust
If the client and contractor have a previous relationship, then there is more confidence in the contractor’s ability to produce quality work.
Drawbacks of Negotiated Tendering:
Low Competition
Since there is no open or selective tendering, negotiated tendering limits the ability to compare the offers available from multiple contractors. This means a greater number of costs are incurred.
Lack of Transparency
Without a formal bidding process, perceptions of favoritism or unfairness could arise; especially in public projects, where impartiality should be fundamental.
Dependence on Contractor
The success of the project relies a lot on the contractor’s expertise and performance. If the wrong contractor is chosen, then it would result in big challenges.
Higher Initial Costs
The contractor may quote higher since there is no competitive pressure that will make them reduce quoted costs.
Limited Innovation
It may be restricted to fewer opportunities to explore differing ideas and solutions, as with fewer contractors participating.
Why the type of tender matters
The tendering method of a construction project is decisive to determine the success of such a project. Every method-in open, selective, and negotiated tendering-has its strength and weakness; therefore, it is important to have an alignment of the type of tender with the goals, complexity, and timeline of the project.
Project Requirements
For open tendering with public sector projects requiring transparency, it is necessary. Whereas for projects demanding special expertise in terms of quality, selective or negotiated tendering will be appropriate.
Budgetary Consideration
Open tendering is always very competitive, and therefore, it is always cost-effective, while negotiated tendering may involve slightly higher costs but yields more customized outcomes.
Risk Mitigation
Selective and negotiated tendering diminishes the risk of an inexperienced contractor executing a project.
Time sensitivity
While negotiability can expedite the overall procuring process, when timing matters, open tendering takes an ample amount of time.
Stakeholder Expectations
These processes should be transparent, and in this regard, accountability is maintained. The best method involved in such cases is open tendering.
Conclusion
It should be noted that the choice of a tendering method is not generic. Negotiated tendering will have specific advantages, like collaborative solutions and faster turn around time. In certain situations, it may result in a lack of competition and transparency. Knowing how to weigh the pros and cons of each method enables a client to make an informed decision that aligns with their project objectives, timeline, and stakeholder expectations. Choosing the right process is the most important step to achieving project success.