In the realm of construction projects, quality control stands as the cornerstone of success. It’s the difference between a structure that stands the test of time and one fraught with defects and deficiencies. From skyscrapers to residential homes, every construction endeavor requires meticulous attention to detail to meet stringent standards and exceed client expectations. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of quality control in construction, exploring its significance, key components, and best practices to ensure excellence at every stage of the project lifecycle.

Understanding the Significance of Quality Control
Quality control encompasses a systematic approach to ensuring that construction projects adhere to predefined standards, specifications, and requirements. It’s not merely about meeting minimum standards but striving for excellence in craftsmanship, durability, and safety. By maintaining rigorous quality control measures, construction firms can safeguard their reputation, mitigate risks, and enhance client satisfaction. After all, a single flaw in construction can have far-reaching consequences, leading to costly rework, legal disputes, and reputational damage.
Key Methods to Ensure Quality Control
Methods to ensure Quality Control
In the dynamic landscape of construction projects, the pursuit of quality excellence stands as a fundamental pillar for success. From towering skyscrapers to intricate residential homes, the adherence to stringent quality standards ensures that structures not only meet but exceed expectations. Quality control serves as the backbone of this endeavor, encompassing a multifaceted approach aimed at upholding standards, mitigating risks, and delivering superior outcomes. In this exploration, we delve into the key components of quality control, unraveling their significance and impact on construction projects.
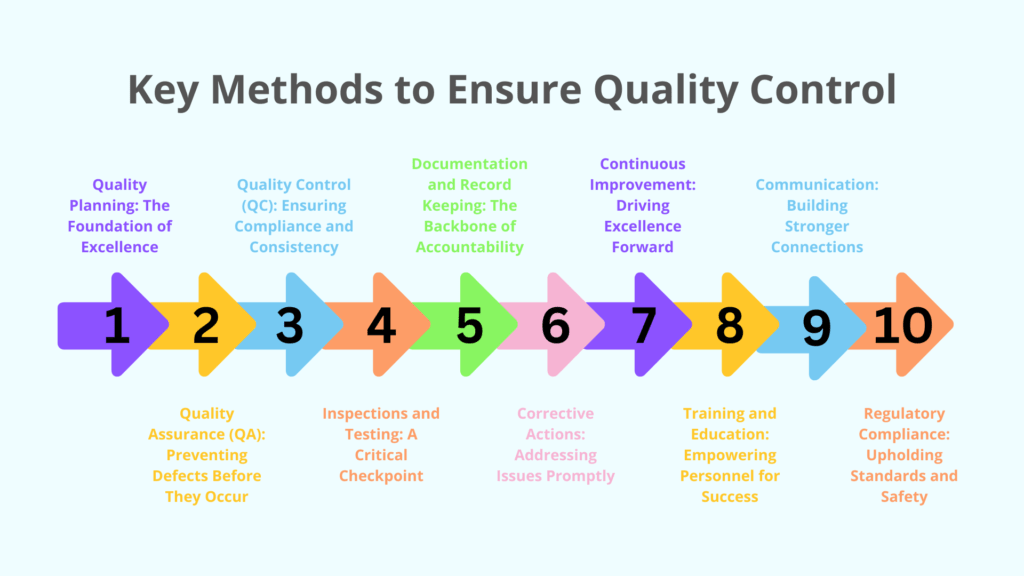
- Quality Planning: The Foundation of Excellence: At the heart of quality control lies meticulous planning. Quality planning involves defining clear objectives, establishing standards, and devising a comprehensive quality management plan. By outlining expectations from the outset, project stakeholders can align their efforts towards achieving excellence. This proactive approach sets the stage for success, laying a solid foundation upon which construction projects can thrive.
- Quality Assurance (QA): Preventing Defects Before They Occur: Quality assurance (QA) encompasses proactive measures aimed at preventing defects before they occur. It involves thorough design reviews, material selection, subcontractor qualification, and adherence to regulatory requirements. By focusing on prevention rather than detection, QA minimizes risks and lays the groundwork for superior construction outcomes. Embracing QA practices ensures that projects are built to last, with an emphasis on durability, safety, and performance.
- Quality Control (QC): Ensuring Compliance and Consistency: Quality control (QC) revolves around monitoring and inspecting construction activities to ensure compliance with established standards. This entails regular site inspections, testing of materials, and verification of workmanship. By identifying deviations early on, QC enables prompt corrective action to maintain quality and mitigate risks. Embracing QC practices ensures consistency and reliability, instilling confidence in clients and stakeholders alike.
- Inspections and Testing: A Critical Checkpoint: Regular inspections are conducted throughout the construction process to identify any deviations from quality standards. This may involve visual inspections, measurements, and testing of materials for strength, durability, and performance. Inspections and testing serve as a critical checkpoint, allowing project teams to identify potential issues and take corrective action swiftly. By prioritizing inspections and testing, construction projects can uphold quality standards and deliver exceptional results.
- Documentation and Record Keeping: The Backbone of Accountability: Accurate documentation of inspections, test results, and non-conformances is essential for tracking the quality of work and addressing any issues that arise. Detailed records provide evidence of compliance with regulatory requirements and serve as a valuable resource for future reference. By maintaining meticulous documentation, construction firms demonstrate accountability and transparency, fostering trust among stakeholders.
- Corrective Actions: Addressing Issues Promptly: When deviations or non-conformances are identified, corrective actions are implemented to address the root cause and prevent recurrence. This may involve rework, repairs, or adjustments to the construction process. Prompt corrective action is essential for maintaining quality and minimizing disruptions to the project timeline. By embracing a proactive approach to corrective actions, construction projects can address issues swiftly and ensure that quality standards are upheld.
- Continuous Improvement: Driving Excellence Forward: Quality control processes should be continuously reviewed and improved to enhance efficiency and effectiveness. Lessons learned from previous projects or quality issues should be incorporated into future projects to prevent similar issues. By embracing a culture of continuous improvement, construction firms can drive excellence forward, evolving their practices to meet evolving standards and expectations.
- Training and Education: Empowering Personnel for Success: Ensuring that personnel involved in the construction project are properly trained and educated on quality standards, procedures, and techniques is essential for maintaining quality throughout the project lifecycle. Investing in training and education empowers individuals to perform their roles with precision and confidence, driving quality excellence across all aspects of the project.
- Communication: Building Stronger Connections: Effective communication among project stakeholders is vital for ensuring that everyone understands quality requirements and expectations. By fostering open channels of communication, construction firms can build stronger connections with clients, contractors, subcontractors, and inspectors, facilitating collaboration and alignment towards common goals.
- Regulatory Compliance: Upholding Standards and Safety: Compliance with applicable building codes, regulations, and industry standards is essential to ensuring the safety, durability, and functionality of the completed structure. By prioritizing regulatory compliance, construction firms demonstrate their commitment to upholding standards and safeguarding the well-being of occupants and communities.
In conclusion, quality control is not a singular task but a multifaceted endeavor that permeates every aspect of construction projects. By embracing the key components of quality planning, assurance, control, inspections, documentation, corrective actions, continuous improvement, training, education, communication, and regulatory compliance, construction firms can uphold standards, mitigate risks, and deliver superior outcomes. In an industry where precision and attention to detail are paramount, effective quality control serves as a cornerstone for success, ensuring that every structure stands as a testament to craftsmanship, safety, and durability.
Major Components of Quality Control
In the dynamic world of construction, quality control stands as a linchpin for success. Whether it’s erecting towering skyscrapers or crafting intricate residential homes, the pursuit of excellence in craftsmanship, safety, and durability is paramount. Effective quality control not only safeguards the reputation of construction firms but also ensures client satisfaction and fosters long-term success. In this blog, we’ll delve into the essential best practices for quality control in construction, outlining strategies to uphold standards, mitigate risks, and deliver superior outcomes.
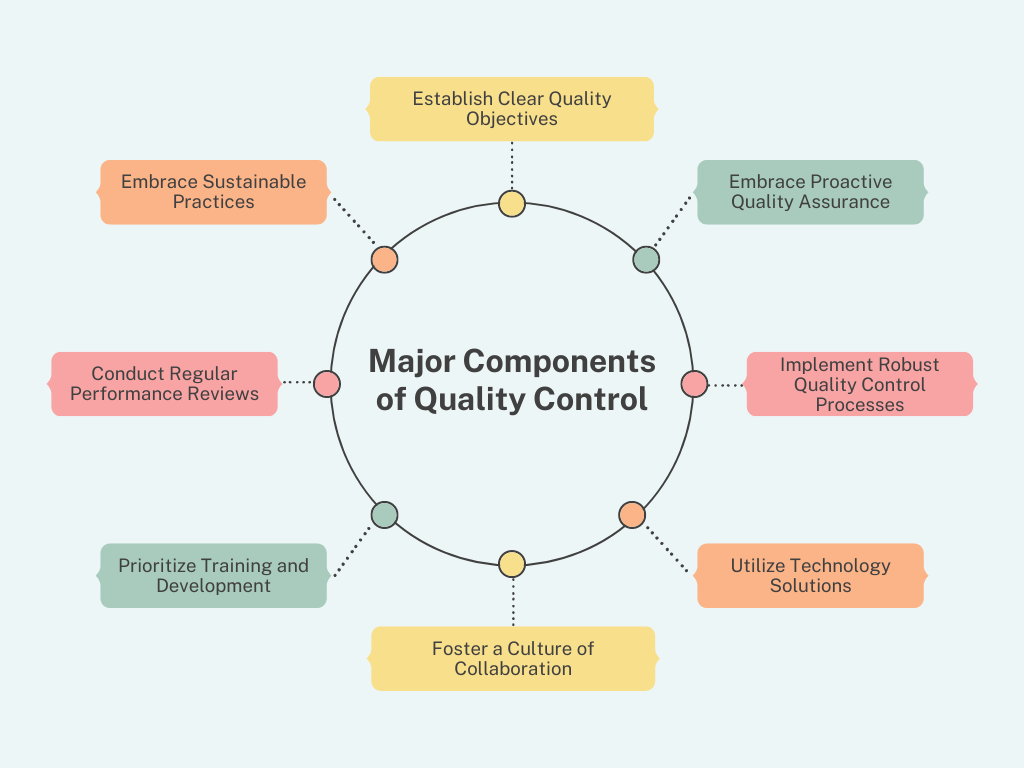
- Establish Clear Quality Objectives: The journey towards quality excellence begins with a clear vision and defined objectives. Construction firms must articulate specific quality goals and communicate them effectively to all stakeholders. Whether it’s achieving zero defects, meeting stringent safety standards, or exceeding client expectations, clarity of purpose serves as a guiding light throughout the project lifecycle.
- Embrace Proactive Quality Assurance: Prevention is often more cost-effective than correction. Quality assurance (QA) involves proactive measures to prevent defects before they occur. This includes comprehensive design reviews, material testing, and subcontractor qualification. By identifying potential risks and addressing them early on, construction firms can minimize rework, delays, and costly disputes.
- Implement Robust Quality Control Processes: Quality control (QC) revolves around monitoring and inspecting construction activities to ensure adherence to established standards. From regular site inspections to meticulous testing of materials and workmanship, QC serves as a critical checkpoint to identify deviations and enforce corrective action. By maintaining a vigilant eye on quality metrics, construction firms can uphold excellence and instill confidence in clients.
- Utilize Technology Solutions: In today’s digital age, technology serves as a powerful ally in enhancing quality control processes. Building Information Modeling (BIM), drones, and construction management software offer innovative solutions for streamlining inspections, monitoring progress, and detecting potential issues. By leveraging technology, construction firms can improve efficiency, accuracy, and collaboration across project teams.
- Foster a Culture of Collaboration: Quality control is not the sole responsibility of a select few but a collective endeavor that involves all project stakeholders. Fostering a culture of collaboration and open communication is essential for identifying and addressing quality issues effectively. By engaging clients, subcontractors, and onsite personnel in quality control processes, construction firms can harness collective expertise and drive continuous improvement.
- Prioritize Training and Development: Investing in the training and development of personnel is paramount for maintaining high-quality standards in construction projects. From skilled laborers to project managers, ensuring that all team members are equipped with the necessary knowledge and skills fosters a culture of excellence. Ongoing training programs, certifications, and skill-building initiatives empower individuals to perform their roles with precision and confidence.
- Conduct Regular Performance Reviews: Continuous improvement lies at the heart of effective quality control. Construction firms should conduct regular performance reviews to assess progress against quality objectives, analyze key performance indicators (KPIs), and identify areas for enhancement. By soliciting feedback from project teams, clients, and other stakeholders, firms can pinpoint opportunities for optimization and drive tangible results.
- Embrace Sustainable Practices: In an era of increasing environmental awareness, sustainability has emerged as a key component of quality control in construction. From green building certifications to eco-friendly materials and practices, integrating sustainable principles into construction projects not only minimizes environmental impact but also enhances long-term durability and resilience. By embracing sustainable practices, construction firms can demonstrate their commitment to quality and environmental stewardship.
Conclusion
Quality control in construction projects is not a mere checkbox but a commitment to excellence in every aspect of the built environment. By integrating rigorous quality control measures into every stage of the project lifecycle, construction firms can deliver superior outcomes that exceed client expectations, uphold safety standards, and stand the test of time. From meticulous planning to continuous improvement, effective quality control is the bedrock upon which successful construction projects are built.