In the dynamic and often complex world of construction management, the principles of lean construction have emerged as a transformative approach to improving efficiency, reducing waste, and delivering greater value to stakeholders. Originating from lean manufacturing principles pioneered by Toyota in the 20th century, lean construction focuses on maximising value for the customer while minimising waste through streamlined processes and continuous improvement. This blog delves into the core concepts of lean construction and its integration with effective project management practices, exploring how these principles are reshaping the construction industry.

Understanding Lean Construction
1. Principles of Lean Construction
Lean construction is grounded in several foundational principles that guide its implementation:
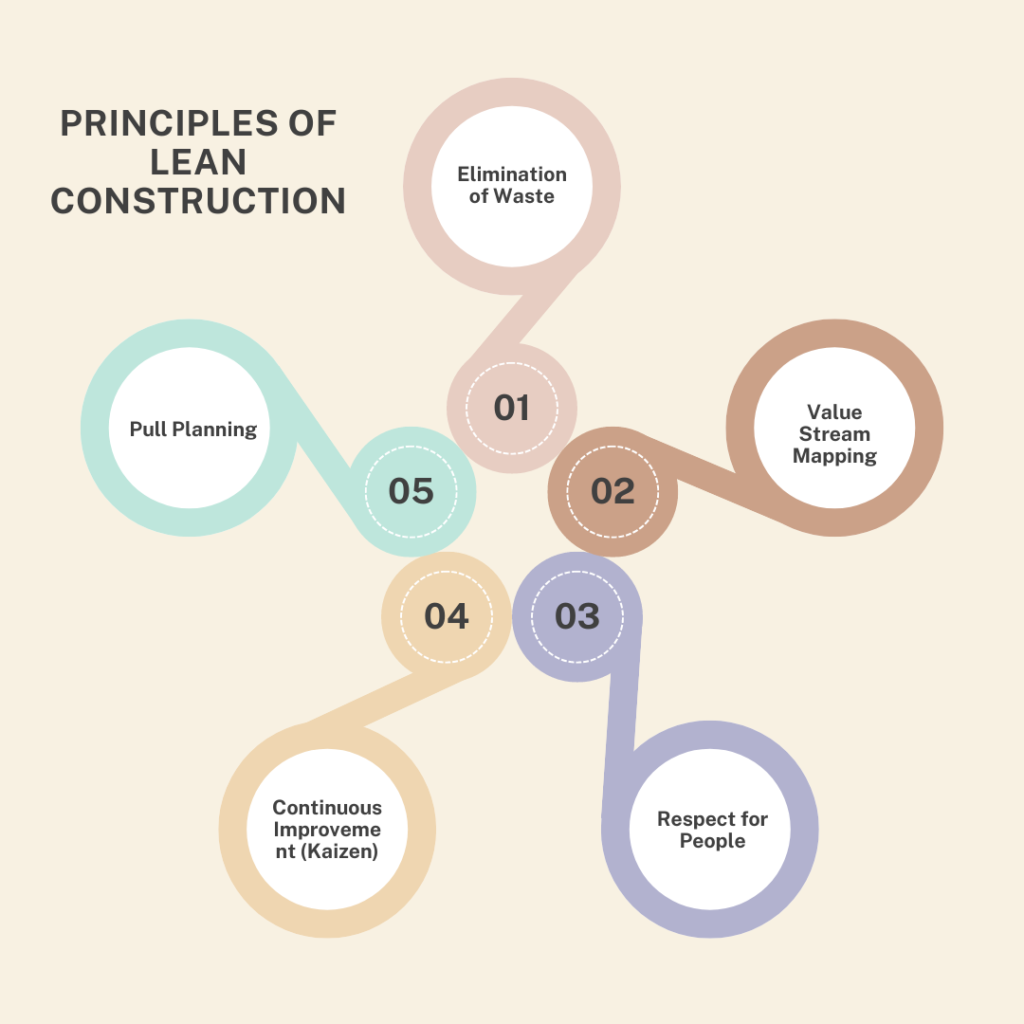
- Elimination of Waste: Waste in construction can take various forms, including overproduction, excess inventory, waiting times, unnecessary movement, defects, and underutilized talent. Lean construction aims to identify and eliminate these sources of waste through systematic analysis and improvement efforts.
- Value Stream Mapping: Similar to its application in manufacturing, value stream mapping in construction involves visualizing and analyzing the flow of materials, information, and activities from start to finish. This technique helps in identifying inefficiencies and optimizing processes to enhance overall project performance.
- Respect for People: Central to lean construction is the principle of respecting and empowering people at all levels of the organization. This involves fostering a culture of collaboration, accountability, and continuous learning, where individuals are encouraged to contribute ideas and improve processes.
- Continuous Improvement (Kaizen): Kaizen, or continuous improvement, is a fundamental aspect of lean construction. It involves systematically identifying opportunities for improvement, implementing changes, and measuring their impact to drive ongoing enhancements in efficiency and quality.
- Pull Planning: Unlike traditional construction scheduling methods that rely on top-down scheduling, pull planning involves collaborative scheduling based on real-time demand and project progress. This approach helps in aligning activities, minimizing delays, and optimizing resource utilization.
2. Practices and Techniques in Lean Construction
Implementing lean construction principles involves adopting specific practices and techniques tailored to the construction industry:
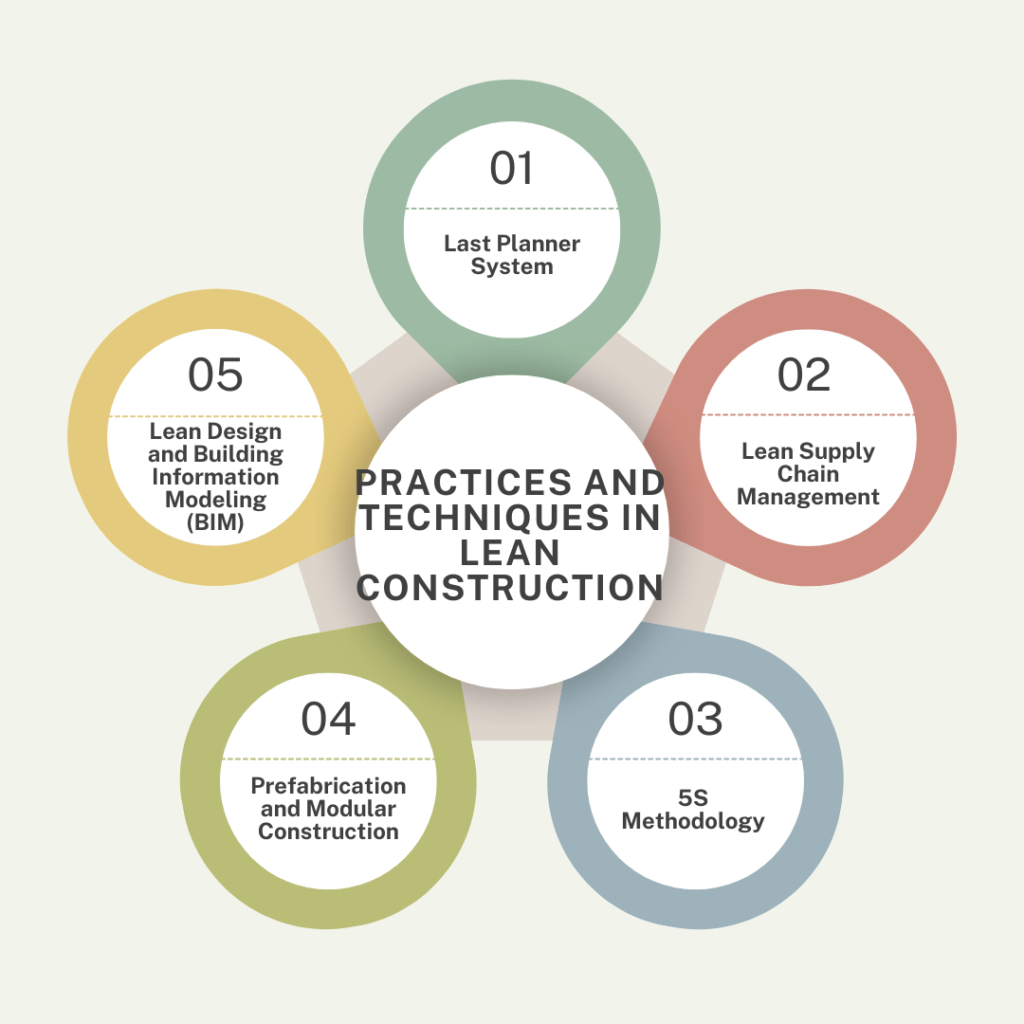
- Last Planner System: The Last Planner System (LPS) is a collaborative approach to project planning and scheduling that involves all stakeholders. It aims to enhance reliability in project delivery by fostering commitment and accountability among team members.
- Lean Supply Chain Management: Efficient supply chain management is crucial in lean construction to ensure timely delivery of materials and minimize inventory waste. This involves strategic sourcing, just-in-time delivery, and building strong relationships with suppliers.
- 5S Methodology: Originating from lean manufacturing, the 5S methodology (Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, and sustain) is applied in construction to organize the workspace, improve safety, and optimize workflow efficiency.
- Prefabrication and Modular Construction: Lean construction encourages the use of prefabrication and modular construction techniques to reduce onsite work, improve quality control, and accelerate project timelines through standardized components.
- Lean Design and Building Information Modeling (BIM): Integrating lean principles with BIM allows for collaborative design and visualization of construction projects, enabling better coordination, reduced errors, and enhanced efficiency throughout the project lifecycle.
Integration with Project Management
1. Project Management and Lean Construction
Effective project management is essential for successfully implementing lean construction principles and achieving project objectives:

- Clear Goals and Objectives: Establishing clear project goals and objectives aligned with customer requirements is essential for prioritizing value and guiding decision-making throughout the project lifecycle.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Engaging stakeholders early and throughout the project promotes collaboration, fosters buy-in, and ensures that project outcomes meet expectations.
- Risk Management: Proactive risk management is critical in lean construction to identify and mitigate potential risks that could impact project timelines, costs, or quality.
- Communication and Collaboration: Open communication and collaboration among project teams, subcontractors, and stakeholders facilitate effective problem-solving, decision-making, and continuous improvement efforts.
- Performance Measurement: Implementing key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics allows project managers to monitor progress, identify areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions to optimize project performance.
2. Benefits of Lean Construction in Project Management
The integration of lean construction principles with effective project management practices offers numerous benefits:
- Enhanced Efficiency: By eliminating waste and optimizing processes, lean construction reduces project lead times, improves resource utilization, and enhances overall project efficiency.
- Cost Savings: Minimizing waste and improving productivity lead to cost savings throughout the project lifecycle, including reduced material waste, lower labor costs, and fewer rework expenses.
- Improved Quality: Lean construction focuses on delivering value and meeting customer expectations, resulting in higher-quality outcomes, reduced defects, and increased client satisfaction.
- Greater Stakeholder Satisfaction: Aligning project goals with stakeholder expectations and delivering projects on time and within budget enhances stakeholder satisfaction and strengthens relationships.
- Sustainable Practices: Lean construction promotes sustainability by minimizing environmental impact, reducing resource consumption, and incorporating sustainable building practices into project designs.
Challenges and Considerations
While lean construction and effective project management offer significant advantages, their implementation can face challenges:

- Cultural Shift: Adopting lean principles requires a cultural shift within organizations, as it involves changing traditional mindsets, practices, and behaviors to foster a collaborative and continuous improvement-oriented environment.
- Complexity of Projects: Construction projects vary in size, scope, and complexity, which can pose challenges in applying standardized lean practices across diverse project types and environments.
- Technology Integration: Leveraging technology and digital tools such as BIM, project management software, and IoT (Internet of Things) solutions is essential for successful lean construction but requires integration into existing workflows and systems.
- Risk Management: Identifying and managing risks specific to lean construction, such as supply chain disruptions, variability in project timelines, and dependency on external factors, is crucial for minimizing potential impacts on project outcomes.
Certainly! Here’s a revised version of the data table without line breaks:
| Category | Description | Key Points/Metrics |
|---|---|---|
| Lean Construction Principles | Fundamental principles guiding lean practices in construction project management. | – Value Maximization, Waste Minimization, Continuous Improvement |
| Lean Methodologies | Techniques and approaches applied to achieve lean objectives in project management. | – Last Planner System, Pull Planning, Target Value Design |
| Tools and Techniques | Specific tools used to implement lean construction in project management. | – A3 Thinking, 5S Methodology, Visual Management |
| Metrics for Performance | Measurement criteria to assess the effectiveness and efficiency of lean project management. | – Percent Plan Complete (PPC), Schedule Variance, Cost Performance Index (CPI) |
| Case Studies and Examples | Real-world examples illustrating successful application of lean in construction projects. | – DPR Construction’s Healthcare Projects, Toyota Production System (TPS) in Construction |
| Challenges and Considerations | Issues and factors that can affect the implementation of lean in construction project management. | – Cultural Resistance, Lack of Training and Education, Integrating Lean with Existing Systems |
| Future Trends and Innovations | Emerging trends and innovations shaping the future of lean construction project management. | – Digitalization and BIM Integration, Lean Supply Chain Management |
Case Studies and Examples
Certainly! Here are some notable Indian case studies where lean construction principles have been successfully applied:
1. Godrej Construction – Vikhroli, Mumbai
Overview: Godrej Construction adopted lean construction principles in the redevelopment of their headquarters in Vikhroli, Mumbai, known as Godrej One. The project aimed to transform their manufacturing facility into a modern office complex while adhering to sustainable practices and optimizing construction processes.

Implementation:
- Last Planner System (LPS): Godrej implemented LPS to improve collaboration among various stakeholders, including architects, engineers, and contractors. This helped in streamlining project schedules and ensuring on-time delivery of milestones.
- Prefabrication and Modular Construction: Lean principles encouraged the use of prefabricated components and modular construction techniques, reducing onsite work and minimizing disruptions. This approach not only accelerated construction timelines but also enhanced quality control and safety measures.
Results:
- The adoption of lean construction practices enabled Godrej Construction to complete the project ahead of schedule and within the allocated budget.
- Improved stakeholder satisfaction due to enhanced project transparency, reduced waste, and optimized resource utilization.
- Godrej One achieved LEED Platinum certification for its sustainable design and construction practices, showcasing its commitment to environmental stewardship.
2. Larsen & Toubro (L&T) – Chennai Metro Rail Project
Overview: Larsen & Toubro (L&T) undertook the Chennai Metro Rail Project, one of India’s largest infrastructure projects, with a focus on lean construction principles to ensure efficient project execution and timely completion.

Implementation:
- Lean Supply Chain Management: L&T implemented robust supply chain management practices, including just-in-time delivery of materials and strategic sourcing, to minimize inventory and reduce project lead times.
- Kaizen Events: Regular kaizen events were conducted to identify and address process inefficiencies, optimize workflows, and enhance productivity across various phases of the project.
Results:
- The Chennai Metro Rail Project was completed ahead of schedule, demonstrating the effectiveness of lean construction practices in accelerating project delivery.
- Improved cost management and budget adherence through waste reduction and streamlined processes.
- Enhanced safety measures and quality standards maintained throughout the construction phases, contributing to overall project success and stakeholder satisfaction.
3. Infosys – Mysore Campus Construction
Overview: Infosys, a leading IT services company in India, employed lean construction principles in the development of its sprawling campus in Mysore, Karnataka. The project aimed to create a sustainable, state-of-the-art facility while optimizing construction processes and minimizing environmental impact.

Implementation:
- Value Stream Mapping: Infosys utilized value stream mapping to analyze and optimize the flow of materials, information, and activities during the construction phase. This helped in identifying bottlenecks and implementing improvements to streamline workflows.
- Lean Design and BIM: Integration of lean design principles with Building Information Modeling (BIM) facilitated collaborative design, visualization, and coordination among project teams, architects, and contractors. This approach ensured design accuracy, reduced errors, and enhanced project efficiency.
Results:
- The Infosys Mysore campus project was completed within the stipulated timeframe and budget, showcasing the effectiveness of lean construction practices in large-scale construction projects.
- Achieved LEED Platinum certification for its sustainable building design and construction practices, emphasizing energy efficiency, water conservation, and environmental sustainability.
- Enhanced employee satisfaction and productivity through the creation of a modern, eco-friendly workspace that promotes innovation, collaboration, and well-being.
4. Mahindra Lifespace Developers – Happinest Avadi, Chennai
Overview: Mahindra Lifespace Developers applied lean construction principles in the development of Happinest Avadi, an affordable housing project in Chennai. The project aimed to deliver high-quality, cost-effective housing solutions while minimizing construction waste and optimizing resource utilization.

Implementation:
- Lean Procurement and Vendor Management: Mahindra Lifespace adopted lean procurement practices to optimize vendor relationships, negotiate favorable terms, and ensure timely delivery of materials. This approach helped in reducing costs and mitigating supply chain risks.
- Continuous Improvement Initiatives: Regular monitoring and improvement initiatives were implemented to enhance construction processes, address challenges, and optimize project schedules. This included conducting regular site assessments, feedback sessions, and training programs for workforce development.
Results:
- Happinest Avadi was completed ahead of schedule and within the allocated budget, demonstrating the efficiency and effectiveness of lean construction practices in affordable housing projects.
- Enhanced customer satisfaction through the delivery of high-quality, sustainable homes that meet the needs and expectations of residents.
- Contribution to community development and social impact by providing affordable housing solutions and promoting inclusive growth in Chennai’s residential real estate market.
Future Trends in Lean Construction and Management
Lean construction is evolving rapidly, with several key trends shaping its future. These trends are driven by the need for efficiency, sustainability, and enhanced project outcomes.
- Adoption of Digital Tools and Technologies : Digital technologies like Building Information Modeling (BIM), Digital Twins, and IoT are increasingly integrated into construction. These tools enhance real-time monitoring, data analysis, and project coordination, aligning with lean principles by reducing waste and improving efficiency.
- Sustainability and Green Construction : Lean construction is progressively focusing on sustainability, integrating eco-friendly practices such as energy efficiency and resource optimization. The future will see lean principles applied to minimize environmental impact, making projects more sustainable while delivering value.
- Collaboration and Integrated Project Delivery (IPD) : Future lean construction will emphasize Integrated Project Delivery (IPD), fostering collaboration among all stakeholders from the project’s start. This approach enhances efficiency and reduces waste by aligning goals and improving communication.
- Modular Construction and Prefabrication : Modular construction and prefabrication methods are gaining traction due to their alignment with lean principles. These techniques reduce on-site waste, improve quality, and shorten timelines, making them integral to the future of lean construction.
- Data-Driven Decision Making : As data becomes more accessible, lean construction will increasingly rely on data-driven decision-making. Advanced analytics, AI, and machine learning will predict outcomes and optimize processes, supporting lean objectives by reducing waste and enhancing efficiency.
These trends highlight the future direction of lean construction, focusing on technological advancements, sustainability, collaboration, and data-driven efficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, lean construction and effective project management represent powerful methodologies for enhancing efficiency, reducing waste, and delivering greater value in the construction industry. By integrating lean principles with robust project management practices, organizations can achieve significant improvements in project outcomes, stakeholder satisfaction, and sustainability performance. While challenges exist, the adoption of lean construction and management continues to evolve, driven by its proven ability to optimize resources, streamline processes, and foster innovation within the built environment.
Through ongoing commitment to continuous improvement, collaboration, and leveraging technology, construction firms can navigate challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and lead the industry towards a more efficient, sustainable, and value-driven future.