Sustainable construction is rapidly becoming a cornerstone of modern development strategies worldwide, and India is no exception. As the country navigates through the challenges of rapid urbanization and industrialization, the construction sector faces the dual challenge of supporting economic growth while minimizing its environmental footprint. In this context, sustainable construction has emerged as a vital approach that promises not only environmental stewardship but also significant economic benefits. This blog delves into the economic insights and benefits of sustainable construction in India, providing a comprehensive overview of why it is critical for the nation’s future.

Introduction
The Indian construction industry is one of the largest in the world, contributing significantly to the nation’s GDP and providing employment to millions. However, it is also one of the most resource-intensive industries, with substantial impacts on the environment. As India continues to urbanize at an unprecedented pace, the demand for infrastructure and housing is skyrocketing. This surge in construction activity, if not managed sustainably, can lead to severe environmental degradation, resource depletion, and long-term economic challenges.
Sustainable construction, which involves creating buildings and infrastructure that are environmentally responsible and resource-efficient, offers a way to mitigate these impacts. By integrating sustainable practices into the construction process, India can ensure that its development is not only economically beneficial but also environmentally sound. This blog explores the various aspects of sustainable construction in India, focusing on its economic benefits, challenges, and the steps that can be taken to mainstream this approach across the country.
Understanding Sustainable Construction
Before delving into the economic benefits, it is essential to understand what sustainable construction entails. Sustainable construction is a holistic approach to building that considers the environmental, social, and economic impacts of construction activities throughout the entire lifecycle of a building—from design and construction to operation, maintenance, and eventual demolition.
Key principles of sustainable construction include:
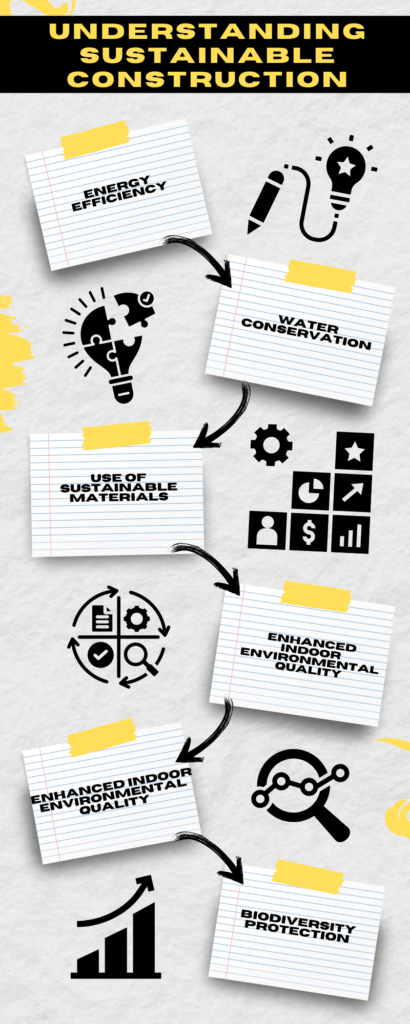
- Energy Efficiency: Minimizing energy consumption through the use of energy-efficient technologies and renewable energy sources.
- Water Conservation: Reducing water usage and promoting the use of recycled water.
- Waste Reduction: Minimizing construction waste through better planning, recycling, and the use of sustainable materials.
- Use of Sustainable Materials: Sourcing materials that are environmentally friendly, such as those with a low carbon footprint or that are recyclable.
- Enhanced Indoor Environmental Quality: Ensuring healthy indoor environments through proper ventilation, natural lighting, and the use of non-toxic materials.
- Biodiversity Protection: Preserving local ecosystems and promoting green spaces around construction sites.
Sustainable construction is not just about reducing the negative impacts of construction; it is also about creating positive outcomes for the environment, society, and the economy. By adopting sustainable construction practices, India can achieve a balance between development and environmental stewardship, ensuring long-term prosperity for future generations.
Economic Insights into Sustainable Construction in India
The economic implications of sustainable construction are far-reaching. While the initial costs of sustainable construction may be higher compared to conventional methods, the long-term economic benefits are substantial. Here are some key economic insights into sustainable construction in India:

1. Cost Savings Through Energy Efficiency
One of the most significant economic benefits of sustainable construction is the reduction in energy costs. Buildings designed and constructed using sustainable construction principles are more energy-efficient, which translates into lower energy bills over the building’s lifetime. In India, where energy costs are a significant concern for both residential and commercial properties, energy-efficient buildings offer a competitive advantage.
For example, sustainable buildings often incorporate advanced insulation, energy-efficient windows, and high-performance HVAC systems that reduce the need for artificial heating and cooling. Additionally, the use of renewable energy sources, such as solar panels, further reduces reliance on fossil fuels, leading to long-term cost savings. In a country like India, where energy demand is growing rapidly, sustainable construction can play a crucial role in managing energy consumption and reducing the overall cost of energy infrastructure.
2. Boosting Local Economies
Sustainable construction also has the potential to stimulate local economies by creating demand for eco-friendly materials and technologies. In India, the construction sector is a major consumer of raw materials, and the shift towards sustainable construction has led to increased demand for materials such as fly ash bricks, recycled steel, and low-VOC paints. These materials are often sourced locally, reducing transportation costs and supporting local industries.
Moreover, sustainable construction projects often require specialized skills and knowledge, leading to the creation of new job opportunities in areas such as green building design, energy auditing, and waste management. By investing in sustainable construction, India can not only reduce its environmental impact but also create a robust market for sustainable products and services, thereby boosting local economies and promoting economic diversification.
3. Increased Property Value
Properties built with sustainable construction practices tend to have higher market values due to their long-term cost savings, reduced environmental impact, and improved living conditions. In India, where real estate is a major investment, the demand for green buildings is on the rise. Buyers and investors are increasingly recognizing the value of sustainable construction, which offers not only lower operating costs but also a healthier living environment.
For developers, sustainable construction can be a selling point that differentiates their projects in a competitive market. Green buildings are often seen as premium properties, attracting higher rents and sale prices. Additionally, sustainable construction can lead to faster occupancy rates, as tenants and buyers are more likely to choose buildings that offer lower utility bills and a better quality of life.
4. Attracting Foreign Investment
India’s commitment to sustainable construction can also attract foreign investment. As global investors become increasingly focused on sustainability, countries that prioritize green building practices are more likely to receive investment. Sustainable construction aligns with the environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria that many international investors use to evaluate potential investments.
By promoting sustainable construction, India can position itself as a leader in sustainable development, attracting environmentally conscious investors and enhancing its reputation on the global stage. This, in turn, can lead to increased foreign direct investment (FDI) in the construction sector, further boosting economic growth.
5. Long-term Economic Stability
Sustainable construction contributes to long-term economic stability by reducing the reliance on non-renewable resources and minimizing operational costs. This is particularly crucial for India, where resource scarcity and fluctuating energy prices pose significant challenges to economic growth. By investing in sustainable construction, India can reduce its vulnerability to resource-related shocks and create a more resilient economy.
Furthermore, sustainable construction practices can help mitigate the financial risks associated with climate change. As extreme weather events become more frequent, buildings that are designed to be resilient to such events are likely to incur lower repair and maintenance costs. This not only protects property values but also reduces the economic impact of natural disasters.
Case Studies
Suzlon One Earth, Pune
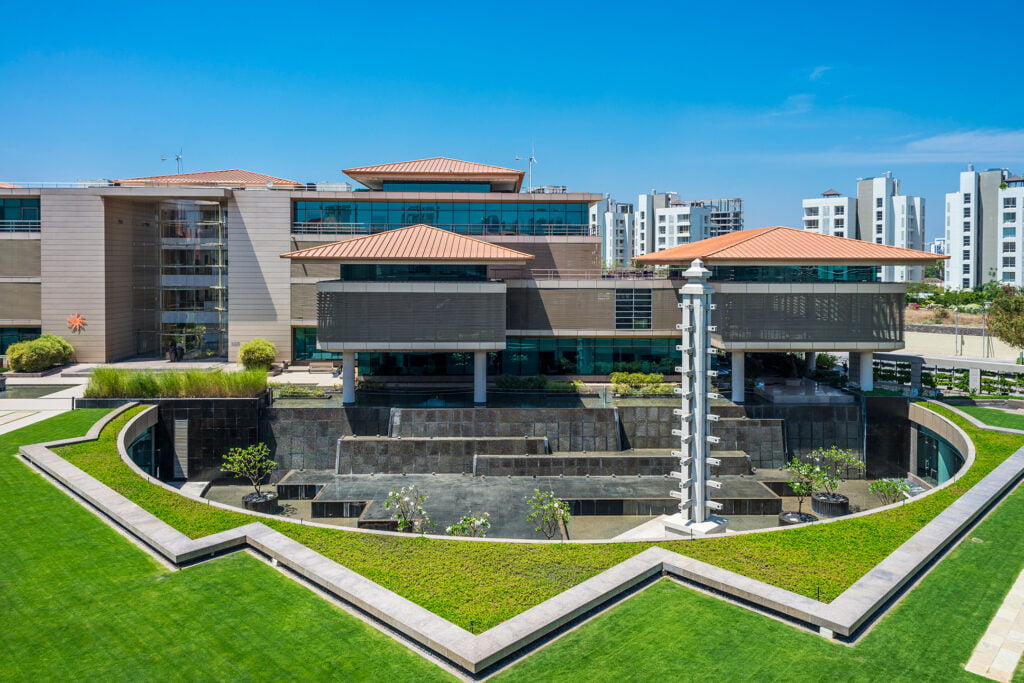

Suzlon One Earth, a LEED Platinum-certified office campus in Pune, Maharashtra, serves as a prime example of sustainable construction in India. The campus features energy-efficient lighting, green roofs, and rainwater harvesting systems, resulting in a 35% reduction in energy consumption and 40% savings in water usage. Over the years, Suzlon One Earth has demonstrated significant operational cost savings and environmental benefits, setting a benchmark for sustainable development in the country .
ITC Green Centre, Gurgaon:

The ITC Green Centre, located in Gurgaon, Haryana, is another notable example of sustainable construction in India. The building incorporates innovative features such as solar panels, daylight harvesting systems, and efficient HVAC systems, resulting in a 45% reduction in energy consumption and 50% savings in water usage. The ITC Green Centre has not only achieved LEED Platinum certification but has also become a symbol of corporate sustainability leadership in India .
Challenges in Implementing Sustainable Construction in India
While the benefits of sustainable construction are clear, there are also several challenges that need to be addressed to mainstream this approach across India. These challenges include:

1. Higher Initial Costs
One of the primary barriers to the adoption of sustainable construction in India is the higher initial cost compared to conventional construction methods. Sustainable construction often requires investment in advanced technologies, high-quality materials, and specialized labor, which can increase the upfront costs of a project. For developers and builders operating on tight budgets, these costs can be prohibitive.
However, it is important to consider the long-term savings and benefits that sustainable construction offers. While the initial costs may be higher, the reduced operating costs, increased property values, and lower environmental impact can offset these expenses over time. Additionally, government incentives and subsidies for sustainable construction can help alleviate the financial burden.
2. Lack of Awareness and Expertise
Another challenge is the lack of awareness and expertise in sustainable construction practices. Many developers, architects, and builders in India are not fully aware of the benefits of sustainable construction or the techniques required to implement it. This knowledge gap can lead to resistance to adopting sustainable practices and a reliance on traditional construction methods.
To overcome this challenge, it is essential to invest in education and training programs that promote sustainable construction practices. By building capacity within the construction industry, India can create a skilled workforce that is capable of designing and constructing sustainable buildings. Additionally, public awareness campaigns can help increase demand for sustainable construction by educating consumers about its benefits.
3. Regulatory and Policy Barriers
The regulatory environment in India can also pose challenges to the adoption of sustainable construction. While there are some policies and regulations in place to promote green building practices, there is still a need for more comprehensive and supportive policies that incentivize sustainable construction.
For example, building codes and standards should be updated to include requirements for energy efficiency, water conservation, and waste reduction. Additionally, government incentives such as tax breaks, subsidies, and grants can encourage developers to invest in sustainable construction. By creating a more supportive regulatory environment, India can accelerate the adoption of sustainable construction practices.
4. Limited Access to Sustainable Materials and Technologies
Access to sustainable materials and technologies is another challenge in India. While there is a growing market for eco-friendly building materials, these products are not always readily available, especially in rural areas. Additionally, the cost of importing sustainable materials and technologies can be prohibitive for many developers.
To address this challenge, it is important to develop local supply chains for sustainable materials and technologies. By supporting local manufacturers and suppliers, India can reduce the cost and increase the availability of sustainable construction products. This, in turn, can make sustainable construction more accessible and affordable for developers across the country.
Steps to Promote Sustainable Construction in India
Despite the challenges, there are several steps that can be taken to promote sustainable construction in India. These steps include:

1. Government Support and Incentives
The government has a crucial role to play in promoting sustainable construction in India. By providing financial incentives, such as tax breaks and subsidies, the government can encourage developers to adopt sustainable construction practices. Additionally, the government can
lead by example by implementing sustainable construction practices in public infrastructure projects.
2. Education and Training Programs
Education and training are essential for building capacity within the construction industry. By offering courses, workshops, and certification programs in sustainable construction, India can create a skilled workforce that is capable of implementing green building practices. Additionally, public awareness campaigns can help increase demand for sustainable construction by educating consumers about its benefits.
3. Development of Sustainable Supply Chains
Developing local supply chains for sustainable materials and technologies is key to making sustainable construction more accessible and affordable. By supporting local manufacturers and suppliers, India can reduce the cost and increase the availability of sustainable construction products. This, in turn, can make sustainable construction more accessible and affordable for developers across the country.
4. Updating Building Codes and Standards
Updating building codes and standards to include requirements for sustainable construction is another important step. By mandating energy efficiency, water conservation, and waste reduction in building codes, the government can ensure that all new construction projects are designed and built with sustainability in mind.
5. Promoting Research and Innovation
Investing in research and innovation is essential for advancing sustainable construction practices in India. By supporting research into new materials, technologies, and construction methods, India can stay at the forefront of sustainable construction and develop solutions that are tailored to the local context.
Conclusion
Sustainable construction in India is not just a trend but a strategic approach to ensuring economic growth while safeguarding the environment. The economic insights and benefits of sustainable construction are clear—cost savings, increased property value, job creation, and attracting foreign investment. By embracing sustainable construction, India can pave the way for a future that is both economically prosperous and environmentally sustainable.
The challenges to adopting sustainable construction in India are real, but they are not insurmountable. With the right policies, incentives, and investments in education and research, India can overcome these challenges and lead the way in sustainable development. Sustainable construction is the key to building a better tomorrow for India, one that harmonizes development with sustainability.
As India continues to grow and urbanize, the choices made today in the construction industry will have long-lasting impacts on the environment, economy, and society. By prioritizing sustainable construction, India can ensure that its development is not only economically beneficial but also environmentally responsible and socially inclusive. Sustainable construction is not just about building for today—it is about building for the future.