What is Economic Order Quantity or EOQ
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is a formula used to determine the optimal order size for materials that minimizes the total costs associated with inventory management, such as ordering and holding costs. In the construction industry, where managing costs and resources is crucial, it helps decide the ideal quantity of materials to order so that projects can proceed smoothly without overspending or running short on supplies.
The goal of using EOQ is to find a balance – ordering enough materials to keep the project moving while avoiding excess stock that ties up cash and adds storage costs. For construction managers, applying economic order quantity means carefully calculating the most cost-effective order size based on factors like the price of materials, the cost of placing orders, and the expense of storing inventory. This approach helps keep projects on budget and reduces the risk of running into supply shortages that can lead to delays.
Importance of Economic Order Quantity
Economic order quantity plays a vital role in construction projects, where managing resources efficiently is key to staying on time and within budget. Here’s why it is important in the construction industry:
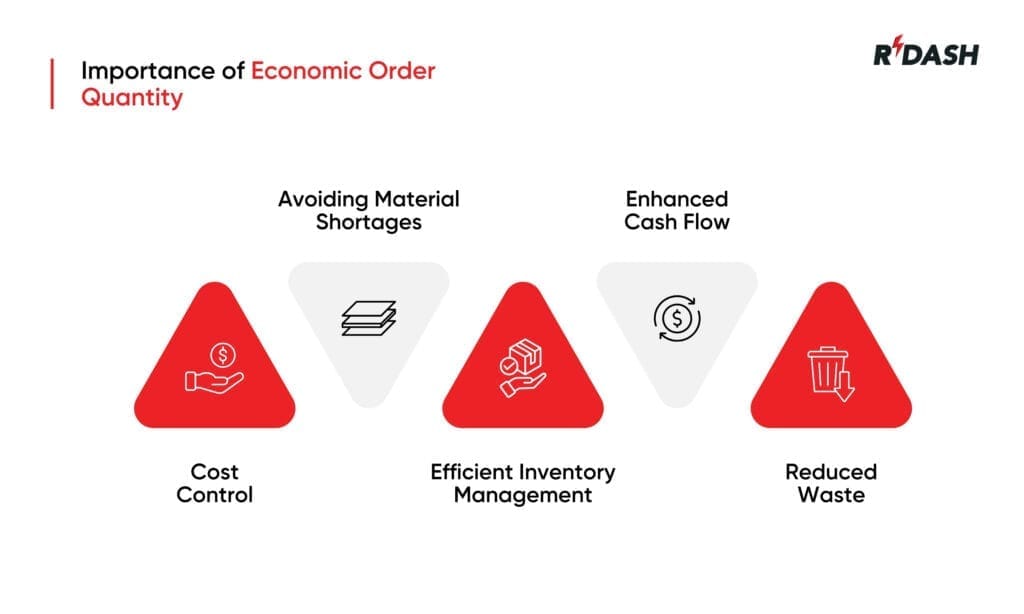
Cost Control: By calculating the optimal order size, EOQ helps construction companies control costs more effectively. When materials are ordered in the right quantities, businesses avoid overspending on bulk orders that may not be immediately needed. It also cuts down on storage costs by preventing excess inventory from piling up on the construction site.
Avoiding Material Shortages: Construction projects need a steady supply of materials to keep progressing. It ensures that orders are placed at the right time and in the right amounts, reducing the chances of running out of critical supplies. This helps maintain the project schedule and prevents costly delays.
Efficient Inventory Management: The construction industry often deals with large volumes of materials, ranging from cement and steel to smaller components like screws and bolts. Using this formula allows for better inventory management by balancing order frequency and storage capacity, making it easier to track materials and ensure that the right amount is available when needed.
Enhanced Cash Flow: Ordering the correct amount of materials helps keep cash flow healthy. Rather than tying up funds in unnecessary stock, businesses can allocate resources to other important areas of the project, such as labor, equipment, or unforeseen expenses.
Reduced Waste: When materials are ordered in the right quantities, there is less chance of leftover supplies going to waste. This not only lowers disposal costs but also supports a more sustainable approach to construction by minimizing excess material use.
Formula for EOQ
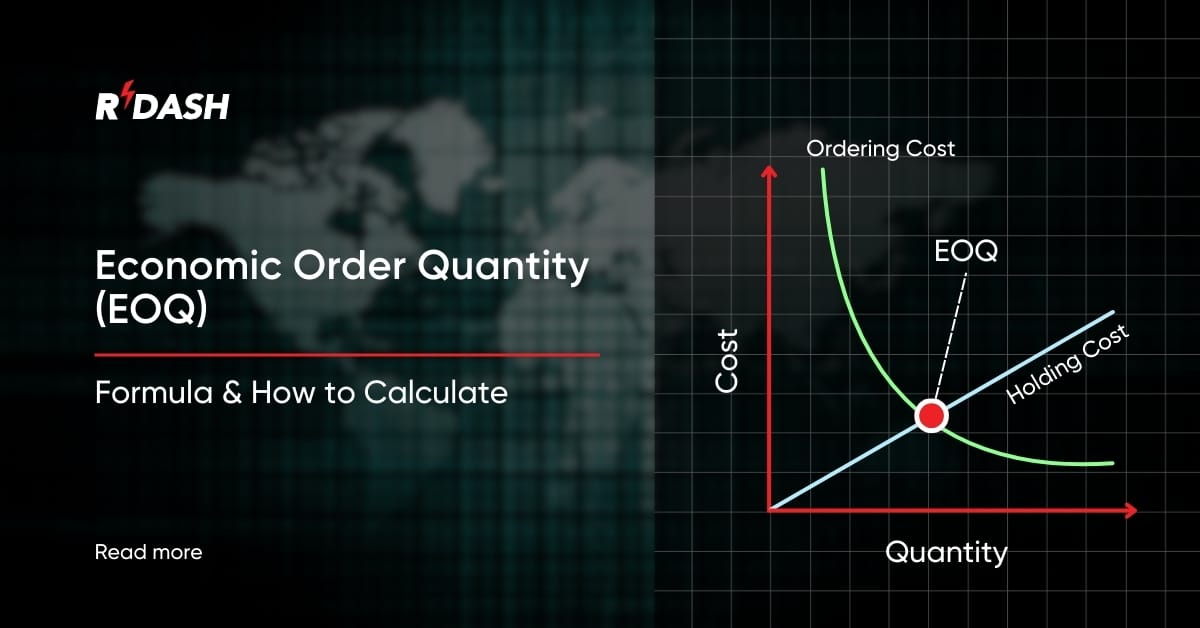
The Economic Order Quantity formula is designed to help determine the ideal order size that minimizes the total costs associated with ordering and holding inventory. The classic EOQ formula is:
EOQ = √(2DS / H)
Where:
- D = Demand, or the total number of units required over a specific period
- S = Ordering cost per order (the cost to place and receive each order)
- H = Holding cost per unit (the cost of storing one unit for a given time)
The formula helps identify the order quantity that results in the lowest combined cost of ordering and holding inventory.
Limitations of EOQ
While EOQ offers several benefits, it’s not without its limitations, especially in the construction industry, where certain variables can complicate inventory management:
Fluctuating Demand: Construction projects often face changes in scope or unforeseen issues that can alter the demand for materials. Calculations rely on consistent demand, so if there are sudden changes in project requirements, the optimal order size determined by EOQ may no longer be accurate.
Variable Costs: Prices for construction materials can fluctuate due to factors like market conditions, seasonal changes, or supply chain disruptions. These variable costs can make it difficult to apply EOQ effectively, as the calculation may not reflect the true cost of materials over time.
Storage Constraints: In some construction projects, space for storing materials may be limited. Even if EOQ suggests an optimal order size, site constraints may require smaller, more frequent deliveries, which can increase costs.
Lead Time Uncertainty: The time it takes for materials to be delivered can vary due to supplier availability or logistical issues. This assumes a consistent lead time, so when there are delays or variations, it can disrupt the supply schedule and impact the project’s progress.
Complex Calculations: It requires detailed information about order costs, holding costs, and demand, which may not always be readily available or accurate in the construction industry. Calculating EOQ can be time-consuming, and errors in the input data can lead to incorrect order quantities.
How to Calculate EOQ
Calculating economic order quantity involves a few straightforward steps using the formula, but you’ll first need to gather some data. Here’s how to do it:
- Determine the Annual Demand (D): Calculate the total quantity of materials or units needed for the project over a year. For construction, this might be the estimated amount of a specific material like concrete or steel.
- Calculate the Ordering Cost (S): Identify the cost associated with placing a single order. This might include expenses related to processing the order, delivery fees, and any administrative costs.
- Identify the Holding Cost (H): Determine the cost to store one unit of inventory for a year. Holding costs can include warehousing fees, insurance, and potential spoilage or obsolescence.
- Plug the Values into the EOQ Formula: Using the EOQ formula, input the demand (D), ordering cost (S), and holding cost (H) to calculate the Economic Order Quantity.
- Adjust as Necessary: In real-world construction projects, you may need to fine-tune the EOQ based on site-specific factors, like storage space limitations, supplier reliability, or fluctuating material costs.
What Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) Can Tell You
The formula is a useful method for improving inventory management, especially in industries like construction, where it is important to balance material costs with storage limitations. Although the calculation is straightforward, its accuracy relies on having correct information about demand, ordering costs, and holding costs. It can serve as a helpful starting point for making inventory decisions, but adjustments are often needed based on real-world conditions to keep projects running smoothly and cost-effectively.
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is a basic supply chain and inventory management concept that calculates the ideal amount of inventory that a business should carry to minimize the overall cost of the inventory, such as holding costs, ordering costs, and shortages. This is how EOQ can enhance your inventory management practice:
Optimal Order Quantity: EOQ calculates the best quantity of goods to order at any one time, allowing companies to reduce the total cost of maintaining inventory.
Minimize Holding Costs: Keeping too much inventory leads to higher storage expenses. EOQ helps find the right balance by maintaining enough stock to meet demand while keeping holding costs as low as possible.
Reduce Ordering Costs: Placing orders too often increases overall costs. EOQ helps reduce these costs by determining the best order frequency, making inventory management more efficient.
Avoid Stock-Outs: EOQ helps determine the optimum order quantity to avoid stockouts to provide a continuous supply to meet customer demand without overages.
FAQs
What is the formula for EOQ?
The formula for EOQ is √(2DS/H), where
D stands for product demand per year.
S is the cost of order.
H = The annual cost of holding each unit.
What motivates EOQ?
EOQ may be influenced by various variables like demand variation, ordering cost variation, and holding cost variation. It may have to be recalculated whenever the parameters vary.
Does EOQ apply to all types of inventory?
EOQ is best applied to inventory with stable, predictable demand, order cost, and holding cost. It may not be appropriate for unstable markets or uncertain demand conditions.
What is the limitation of EOQ?
The largest drawback of EOQ is that it presumes that demand, holding cost, and order cost are fixed, and this may not be the case for every company. Further, it doesn’t take into account potential bulk discounts, storage capacity, or budgetary constraints that can affect ordering.
Embracing and implementing EOQ can go a long way in simplifying your inventory procedures, resulting in greater cost savings and operating efficiency. It is, nonetheless, important to customize EOQ calculations to fit the unique circumstances of your company and market condition.
Next Read: What is Sustainable Construction (Challenges & Benefits)