EMD (Earnest Money Deposit) in the construction industry is a pivotal concept that helps establish trust and commitment between the parties involved in a project. It is a deposit made by a contractor, developer, or investor to show their genuine interest in proceeding with a construction contract or bid. The EMD acts as a financial assurance that the party is serious about their intent and will not withdraw after the agreement is finalized. Understanding the intricacies of EMD is essential for navigating the complex landscape of construction contracts and bids. This blog delves into the significance of EMD, outlines best practices, and explores its impact on various stakeholders in construction projects.
What is Earnest Money Deposit ?
An Earnest Money Deposit is a sum of money provided by a buyer to a seller as a show of good faith in a transaction. In the context of construction, Earnest Money Deposit is typically submitted by contractors or bidders during the tendering process for construction projects. This deposit serves as a guarantee that the bidder is serious about their proposal and intends to comply with the terms of the bid if awarded the contract.

Importance of Earnest Money Deposit in Construction
Earnest Money DD holds significant importance in the construction industry for several reasons:

- Demonstrates Commitment: By providing an Earnest Money Deposit , bidders demonstrate their serious intent to participate in the project and adhere to the bidding process.
- Mitigates Risks for Owners: Earnest Money Deposit helps protect project owners from frivolous or non-serious bids, ensuring that only genuine contractors participate in the bidding process.
- Enhances Credibility: Bidders who provide Earnest Money Deposit are seen as more credible and trustworthy, which can enhance their reputation and increase their chances of winning contracts.
- Financial Security: In the event that a winning bidder fails to fulfill their obligations, the Earnest Money Deposit can be forfeited, providing financial compensation to the project owner.
How Earnest Money Deposit Works in Construction Projects
The process of Earnest Money Deposit in construction projects typically involves the following steps:

- Tender Announcement: The project owner announces a tender or request for proposal (RFP), outlining the project details and requirements, including the Earnest Money Deposit amount.
- Bid Submission: Interested contractors submit their bids along with the required Earnest Money Deposit. The Earnest Money Deposit amount is usually a fixed percentage of the project’s estimated cost.
- Bid Evaluation: The project owner evaluates the bids based on various criteria such as price, technical expertise, and compliance with project requirements.
- Contract Award: The contract is awarded to the selected bidder. If the winning bidder accepts the contract terms, the Earnest Money Deposit is either refunded or adjusted against the contract amount.
- Forfeiture of Earnest Money Deposit: If the winning bidder fails to comply with the contract terms or withdraws their bid, the Earnest Money Deposit may be forfeited as compensation to the project owner.
Best Practices for Managing Earnest Money Deposit in Construction
To effectively manage Earnest Money Deposit in construction projects, consider the following best practices:

- Clearly Define Earnest Money Deposit Requirements: Ensure that the tender documents clearly specify the EMD amount, acceptable forms of payment (e.g., bank guarantee, cashier’s check), and conditions under which the Earnest Money Deposit may be forfeited or refunded. Clarity in Earnest Money Deposit requirements helps avoid disputes and misunderstandings.
- Set Appropriate Earnest Money Deposit Amounts: The Earnest Money Deposit amount should be substantial enough to ensure bidder commitment but not so high that it discourages participation. Typically, Earnest Money Deposit amounts range from 1% to 5% of the project’s estimated cost, depending on the project size and complexity.
- Transparent Evaluation Process: Maintain transparency in the bid evaluation process to build trust and confidence among bidders. Clearly communicate the criteria for bid evaluation and ensure that all submitted bids are assessed fairly and impartially.
- Timely Refunds: For unsuccessful bidders, ensure that Earnest Money Deposit refunds are processed promptly after the contract is awarded. Delays in Earnest Money Deposit refunds can strain relationships and deter contractors from participating in future tenders.
- Forfeiture Procedures: Establish clear procedures for Earnest Money Deposit forfeiture, specifying the conditions under which the deposit will be forfeited. This can include scenarios such as withdrawal of bid, failure to sign the contract, or non-compliance with contractual obligations.
- Record Keeping: Maintain accurate records of all Earnest Money Deposit transactions, including the amount received, date of receipt, and refund or forfeiture details. Proper record-keeping helps in tracking Earnest Money Deposit and resolving any disputes that may arise.
Impact of Earnest Money Deposit on Various Stakeholders
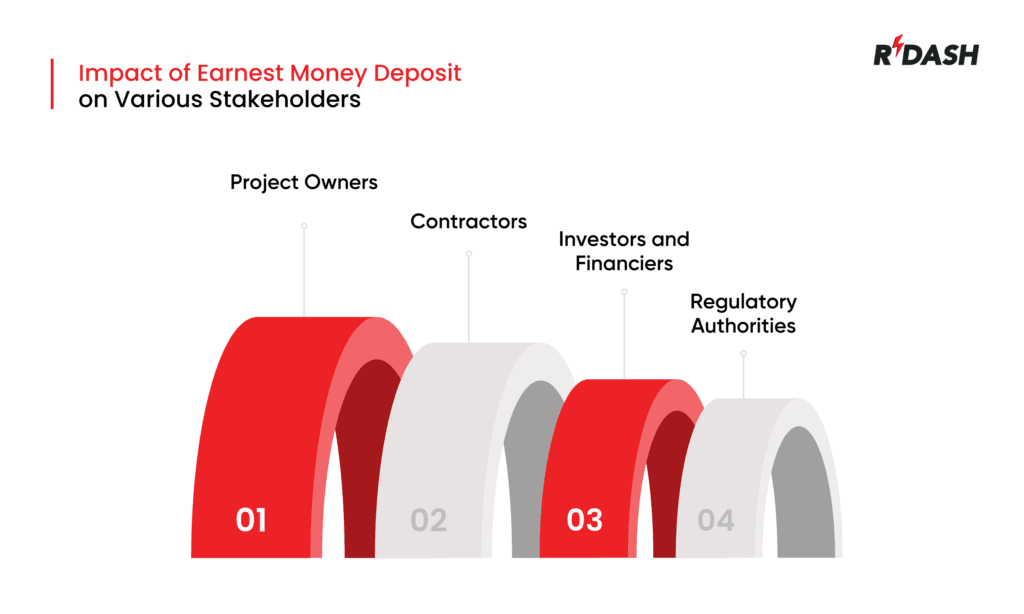
- Project Owners: For project owners, EMD provides financial security and ensures that only serious bidders participate in the tendering process. This reduces the risk of project delays and cost overruns due to non-compliance by contractors.
- Contractors: For contractors, EMD represents a financial commitment and a demonstration of their seriousness and credibility. However, it also entails a financial risk, as the EMD may be forfeited if they fail to meet the contract terms. Contractors need to carefully assess their ability to fulfill project requirements before submitting bids with EMD.
- Investors and Financiers: Investors and financiers view EMD as an indicator of a contractor’s financial stability and commitment to the project. A well-managed EMD process can enhance investor confidence and facilitate project financing.
- Regulatory Authorities: Regulatory authorities may establish guidelines for EMD amounts and procedures to ensure fairness and transparency in the tendering process. Compliance with these guidelines is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the construction industry.
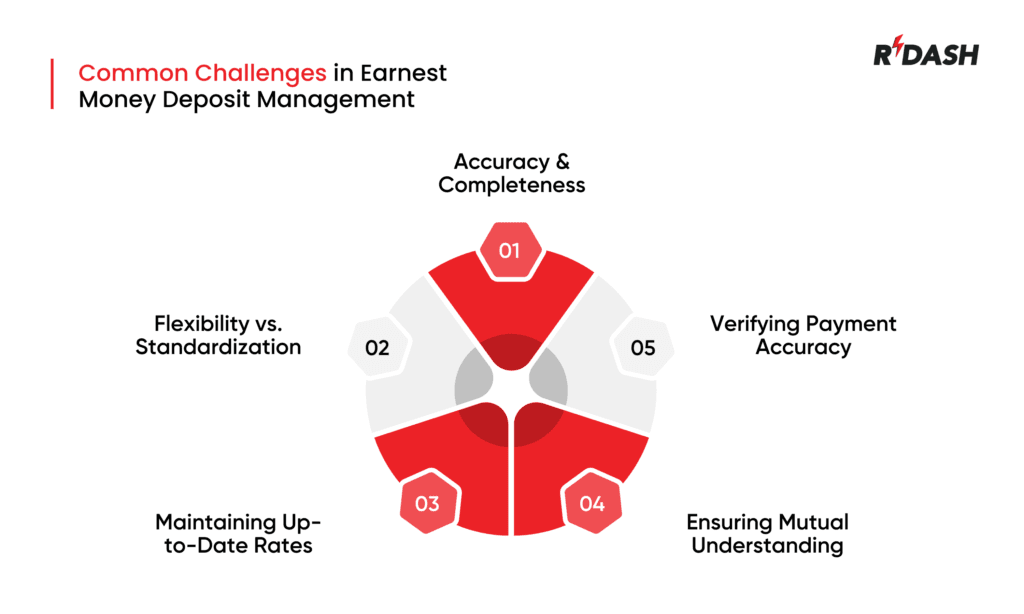
Taming the Tangles: Overcoming Common Challenges in Earnest Money Deposit Management
The Schedule of Rates (SOR) – a cornerstone document in construction projects – can be a powerful tool for ensuring transparency, fairness, and cost-effectiveness. However, effective EMD (Electronic Management of Documents) of SORs presents its own set of challenges. Here, we explore some of the most common roadblocks and strategies to navigate them:
Challenge 1: Accuracy and Completeness
EMD systems rely on accurate and comprehensive data entry. Inconsistent descriptions, missing units of measurement, or outdated rates can lead to costly misunderstandings and delays.
Solution:
- Standardized Templates: Implement standardized templates for EMD entry, pre-populated with common items and units.
- Collaboration: Encourage collaboration between project managers, estimators, and quantity surveyors during data entry.
- Regular Reviews and Audits: Schedule regular reviews to ensure data accuracy and conduct periodic audits to identify and rectify any discrepancies.
Challenge 2: Flexibility vs. Standardization
While standardization streamlines Earnest Money Deposit, construction projects often require unique elements. Rigid systems may not accommodate these variations.
Solution:
- Customization Options: Allow for customization within the EMD system to incorporate project-specific details while maintaining the core structure of the SOR.
- Addendums and Supplementary Agreements: Utilize addendums and supplementary agreements to address unforeseen circumstances without compromising the core SOR.
Challenge 3: Maintaining Up-to-Date Rates
Market fluctuations and technological advancements necessitate regular updates to the SOR to reflect current costs. Outdated rates can lead to inflated project budgets or underestimation of costs for contractors.
Solution:
- Automated Notifications: Implement automated notifications to alert project managers when rates approach pre-determined thresholds, triggering a review process.
- Market Research and Analysis: Conduct regular market research and analysis to track price changes for relevant materials and labor.
- Version Control: Maintain version control within the EMD system to track changes in rates over time and ensure clarity for referencing historical data.
Challenge 4: Ensuring Mutual Understanding
Effective communication and clear understanding of the SOR are crucial. Ambiguous terms or interpretations can lead to disputes during project execution.
Solution:
- Detailed Explanations: Include detailed explanations within the SOR for complex items or specific methodologies.
- Training and Workshops: Conduct training sessions and workshops for stakeholders involved in the project to ensure a shared understanding of the SOR.
- Open Communication Channels: Encourage open communication channels for contractors to clarify any potential discrepancies before work commences.
Challenge 5: Verifying Payment Accuracy
Reconciling invoices and ensuring accurate payments can be complex with large, data-heavy EMD systems. Errors or inconsistencies can lead to disputes and delays.
Solution:
- Standardized Invoice Formats: Enforce standardized invoice formats that align with the structure of the SOR for easy cross-referencing.
- Automated Calculations: Utilize automated calculations within the EMD system to minimize human error during payment processing.
- Detailed Payment Reports: Generate detailed payment reports that clearly show the breakdown of costs and quantities for each item.
Case Studies: Earnest Money Deposit in Construction Projects

Case Study 1: Public Infrastructure Project
In a large public infrastructure project, the government agency required an EMD of 2% of the project’s estimated cost. By clearly defining the EMD requirements and maintaining transparency in the evaluation process, the agency attracted multiple credible bidders. The selected contractor successfully completed the project, and the EMD was adjusted against the final payment.
Case Study 2: Residential Development
A private developer initiated a tender for a residential development project, requiring an Earnest Money D of 5% of the project cost. Due to the high EMD amount, participation was limited to larger contractors. To address this, the developer revised the EMD requirement to 3% and accepted bank guarantees. This adjustment increased participation and resulted in a competitive bidding process.
Case Study 3: International Construction Project
An international construction project faced challenges with Earnest Money Deposit due to currency fluctuations. The project owner addressed this by accepting EMD in multiple currencies and using forward contracts to hedge against currency risk. This approach provided flexibility for international bidders and ensured a smooth EMD process.
Conclusion
Earnest Money Deposit (EMD) is a vital component of construction project management, ensuring bidder commitment and protecting project owners from non-serious bids. By understanding the significance of EMD, implementing best practices, and addressing common challenges, stakeholders can enhance the efficiency and transparency of the tendering process. Effective EMD management not only fosters trust and credibility but also contributes to the successful execution of construction projects.
As the construction industry continues to evolve, staying informed about EMD practices and adapting to changing market conditions will be crucial for all stakeholders. By prioritizing clear communication, transparency, and fairness, the construction industry can leverage EMD to build stronger, more resilient project frameworks and achieve sustainable growth.