What is Centering in Construction
In construction, centering refers to the temporary framework used to support arches, vaults, and other structures while concrete or mortar they are made from sets and hardens. This framework is crucial as it holds the material in place, maintaining the desired shape and ensuring that the structure’s integrity is not compromised during the critical setting phase.
Importance of Centering in Construction
Centering in construction process is vital for multiple reasons, each contributing to the final quality and safety of the building:
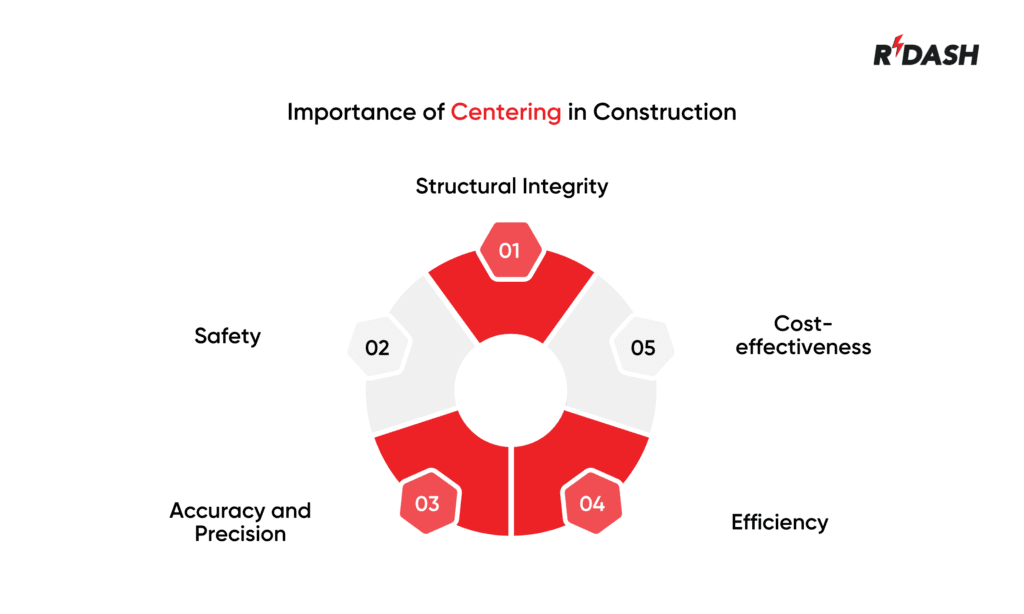
- Structural Integrity: Centering supports structures during the vulnerable phase when the concrete or mortar is not yet capable of supporting itself. This support is essential to prevent the structure from collapsing, which can lead to severe structural failures.
- Safety: Properly installed centering contributes to safety on the construction site by preventing premature collapses that could endanger workers and result in costly damages.
- Accuracy and Precision: Centering ensures that the construction adheres to the architectural specifications. It helps maintain precise alignments and uniformity in the shapes and dimensions of arches and other features, which are critical for both aesthetics and structural reasons.
- Efficiency: Using centering can speed up the construction process by allowing simultaneous work on different parts of the structure. It enables quicker setting and curing of concrete, thereby reducing the overall construction time.
- Cost-effectiveness: Efficient use of centering can also be cost-effective. By reducing errors and the need for reworks, it saves materials, labor, and time, all of which contribute to the cost of construction.
The Role of Centering in Construction
In construction, centering plays a pivotal role, especially in the building of structures that require precise curvature and structural integrity, such as arches, domes, and bridges. This formwork system ensures the concrete or other materials are supported during the hardening process until they can support themselves. Here’s a deeper look at its significance:
- Ensuring Structural Integrity: Centering is crucial for maintaining the shape and strength of a structure until the concrete achieves sufficient hardness. It prevents the structure from collapsing under its own weight or under environmental stresses such as wind or vibrations.
- Support and Alignment: It provides a mold for concrete or other materials, helping maintain alignment and shape according to the architectural specifications, thereby avoiding deviations that could affect structural integrity.
- Aesthetic and Functional Accuracy: Proper centering affects both the aesthetics and functionality of a building. It ensures that the architectural designs are followed to precision, reflecting the intended visual and functional outcomes.
Types of Centering in Construction:
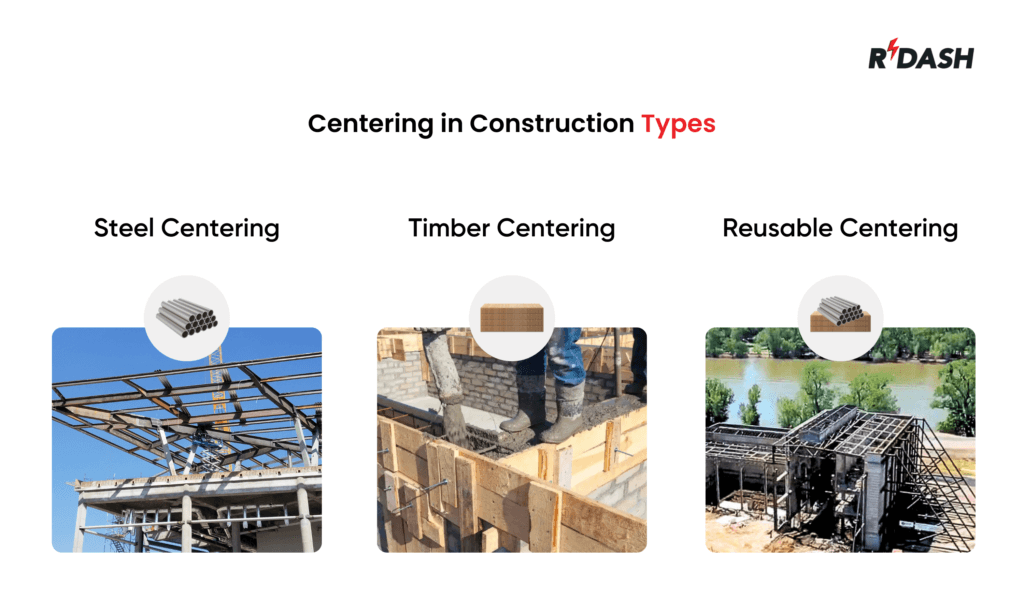
- Steel Centering: This is preferred in heavy construction due to its robustness and ability to be reused multiple times. Steel centering can withstand considerable weight, making it ideal for large-scale constructions.
- Reusable Centering: Made from various materials, including metal and plastic, reusable centering is designed for multiple uses, making it a cost-effective and sustainable option in construction projects.
- Timber Centering: While being less durable than steel, timber centering is cost-effective for smaller projects or in regions where timber is plentiful. It’s easier to cut and assemble but requires careful handling to maintain its effectiveness.
Each type of centering material offers distinct advantages and can be selected based on specific project needs, environmental conditions, and budget constraints. Understanding these options helps in selecting the most appropriate and efficient centering method for any construction project, ensuring safety, precision, and durability of the structure.
Difference Between Formwork, Shuttering, and Centering in Construction
In the construction industry, the terms formwork, shuttering, and centering are often used interchangeably, but they refer to different aspects of construction and serve distinct purposes. Understanding these differences is crucial for anyone involved in building and construction projects.
Formwork: Formwork is used in concrete construction as either temporary or permanent molds into which concrete or similar materials are cast. It serves as the container that shapes the concrete into the desired structural form. This system serves as a casing for the concrete until it hardens and acquires structural integrity. Formwork can be made using a variety of materials including steel, plywood, aluminum, or composite materials, and it can be used for both structural and non-structural elements.
Shuttering: Shuttering is a type of formwork. Specifically, it refers to the method of forming molds using rigid materials that hold the concrete in place during the curing process and until it hardens sufficiently. The term “shuttering” is generally used in the United Kingdom and the Indian subcontinent. Shuttering is usually temporary and made from materials like plywood or timber, which are easy to dismantle.
Centering: Centering specifically refers to the part of formwork used for supporting horizontal forms such as slabs, beams, and flat concrete surfaces. It’s essentially the support system that holds up the formwork used for laying slabs and beams. The materials for centering can be traditional wood or metal props depending on the scale of the project and the load requirements.
Key Differences:
- Application: Formwork is used for all types of concrete moldings, shuttering is specifically a method within formwork for erecting vertical structures, and centering is used for supporting horizontal structures.
- Material: While formwork can be made of a variety of materials including sophisticated composites and metals, shuttering typically involves more robust materials like steel and plywood to contain concrete. Centering, on the other hand, often uses simpler, less robust materials since it primarily serve as support.
- Reusability: Metal and composite formworks are designed for reuse, offering more durability as compared to the typically wooden shuttering.
- Construction Phase: Shuttering and centering are part of the formwork phase but are applied at different construction stages and serve different structural functions.
FAQs
What materials are commonly used for centering?
Centering can be constructed from a variety of materials including traditional timber, as well as steel and aluminum frameworks which are becoming more popular due to their reusability and strength.
How is centering designed?
The design of centering depends on the load it needs to support, the span of the structure, and the specific requirements of the project. Engineers typically calculate the loads and stresses to determine the best material and configuration.
Can centering be reused?
Yes, especially when made from materials like metal or reusable formwork systems. However, the reusability also depends on how carefully the centering is dismantled after the concrete cures.
How is centering removed?
Centering is carefully removed once the concrete achieves sufficient strength to support itself. This process, known as striking or de-shuttering, must be done cautiously to prevent damage to the concrete structures.
What are the risks of improper centering?
Improper centering can lead to structural failures like sagging or collapse during the concrete curing process. It is crucial to ensure that the centering is correctly designed and securely installed to avoid such risks.