Prefabricated Structures, also known as off-site construction, involves manufacturing building components or entire structures in a controlled factory environment before transporting them to the construction site for assembly. This method diverges from traditional on-site construction practices, where materials are brought to the site and assembled piece by piece. The advantages of prefabrication are manifold, offering enhanced efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability while mitigating many challenges associated with conventional construction techniques.

In recent years, the construction industry in India has witnessed a significant shift towards innovative and efficient building practices. Among these, prefabricated structures have emerged as a game-changer, offering numerous advantages over traditional construction methods. As urbanization accelerates and the demand for infrastructure and housing grows, prefabricated structures provide a compelling solution for developers and contractors in India. This blog explores the rise of prefabricated structures in construction, their benefits, cost implications, and their relevance to the Indian market, along with some notable examples.
Understanding Prefabricated Structures in Construction

Prefabricated structures, also known as prefab or modular buildings, are manufactured off-site in a controlled factory environment and then transported to the construction site for assembly. This approach differs from traditional construction, where buildings are constructed entirely on-site. The prefabrication process involves producing various components or modules of a building, such as walls, floors, and roofs, which are then assembled like a puzzle on the construction site.
This method has gained traction in India due to its efficiency, speed, and ability to reduce waste and environmental impact. Prefabricated structures are particularly well-suited for projects that require rapid construction or face challenges such as difficult terrain, tight deadlines, or limited on-site labor availability.
Benefits of Prefabricated Structures
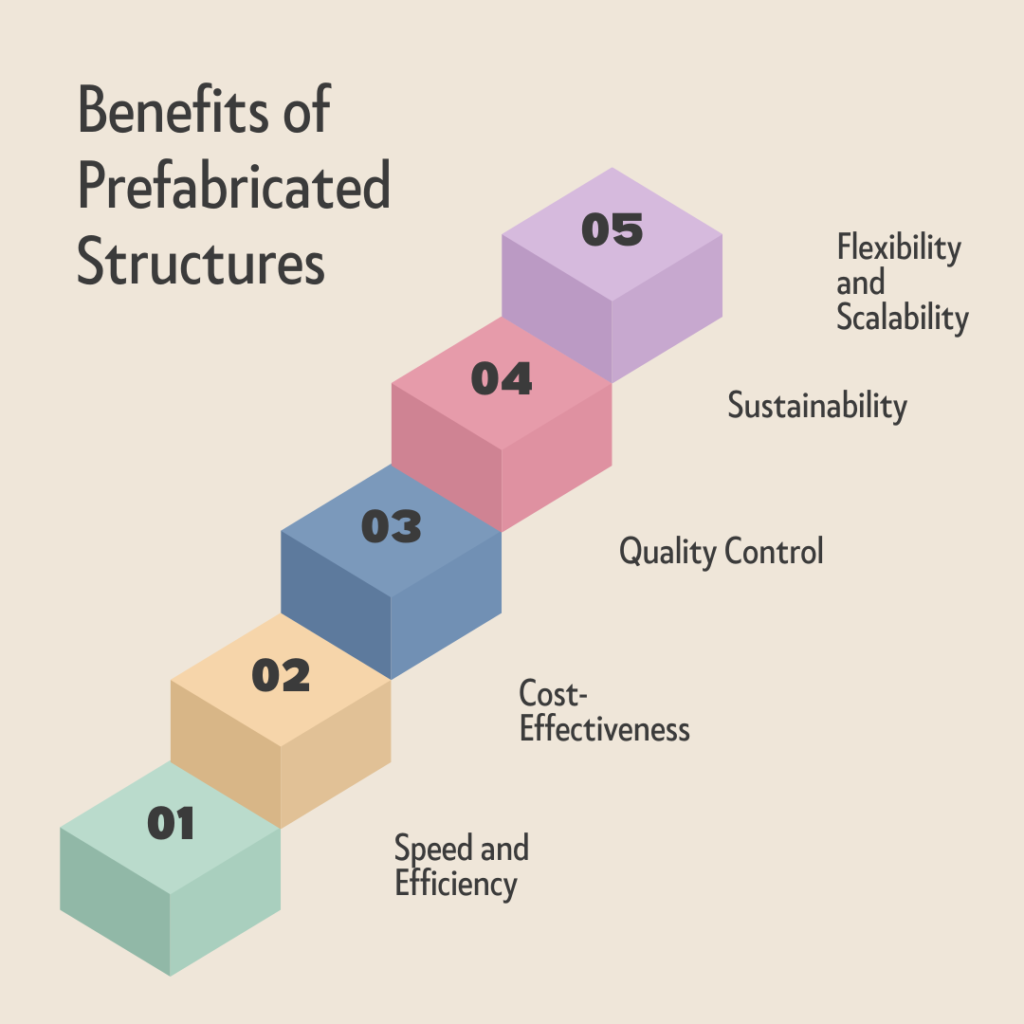
- Speed and Efficiency: One of the most significant advantages of prefabricated structures is the speed of construction. Since components are manufactured in a controlled environment, construction timelines can be significantly reduced. This is particularly beneficial for large-scale projects or those with tight deadlines.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Prefabricated structures can reduce costs in several ways. Manufacturing components off-site minimizes waste and allows for bulk purchasing of materials, leading to cost savings. Additionally, the reduced construction time lowers labor costs and other associated expenses, such as equipment rentals.
- Quality Control: Prefabrication takes place in a controlled factory environment, ensuring consistent quality and precision. This reduces the likelihood of errors and defects, leading to higher-quality construction outcomes.
- Sustainability: Prefabricated structures are inherently more sustainable than traditional construction methods. The controlled manufacturing process reduces material waste, and the use of recycled materials is more feasible. Moreover, less on-site construction means reduced noise, dust, and environmental disruption.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Prefabricated structures offer flexibility in design and scalability. Modules can be easily added or removed to accommodate changing needs. This is particularly useful for projects that may require future expansion or modifications.
Prefabricated Structures in India: Current Trends and Adoption
The adoption of prefabricated structures in India is on the rise, driven by several factors, including the need for affordable housing, rapid urbanization, and government initiatives promoting sustainable and smart cities. In recent years, the Indian government has actively encouraged the use of prefabricated construction methods to meet the country’s growing infrastructure demands.
Examples of Prefabricated Structures in India

- Affordable Housing Projects: The Indian government has launched several affordable housing schemes to address the housing shortage in urban areas. Prefabricated structures are increasingly being used in these projects due to their cost-effectiveness, speed, and ability to meet strict deadlines. For example, in states like Maharashtra and Gujarat, prefabricated techniques have been employed to construct thousands of affordable housing units.
- Infrastructure Development: Prefabrication has also found applications in infrastructure projects such as bridges, flyovers, and metro rail systems. The Bangalore Metro and Delhi Metro projects have utilized prefabricated components for their construction, significantly reducing on-site construction time and minimizing disruption to city life.
- Commercial and Office Buildings: Several commercial and office buildings in India are now being constructed using prefabricated methods. This trend is particularly prominent in tier-2 and tier-3 cities, where the demand for modern office spaces is growing. Prefabricated structures offer the flexibility to quickly set up new office spaces, meeting the needs of businesses looking to expand rapidly.
- Hospitality and Tourism: In India’s hospitality and tourism sector, prefabricated structures are gaining popularity for constructing resorts, hotels, and eco-friendly accommodations. Prefabrication allows developers to create unique, sustainable, and aesthetically pleasing structures in remote or challenging locations, catering to the growing demand for eco-tourism.
Prefabricated Structures Cost in India
The cost of prefabricated structures in India varies depending on several factors, such as the type of structure, materials used, and project location. Generally, prefabricated construction is considered more cost-effective than traditional methods due to reduced labor costs, faster construction times, and lower material waste.
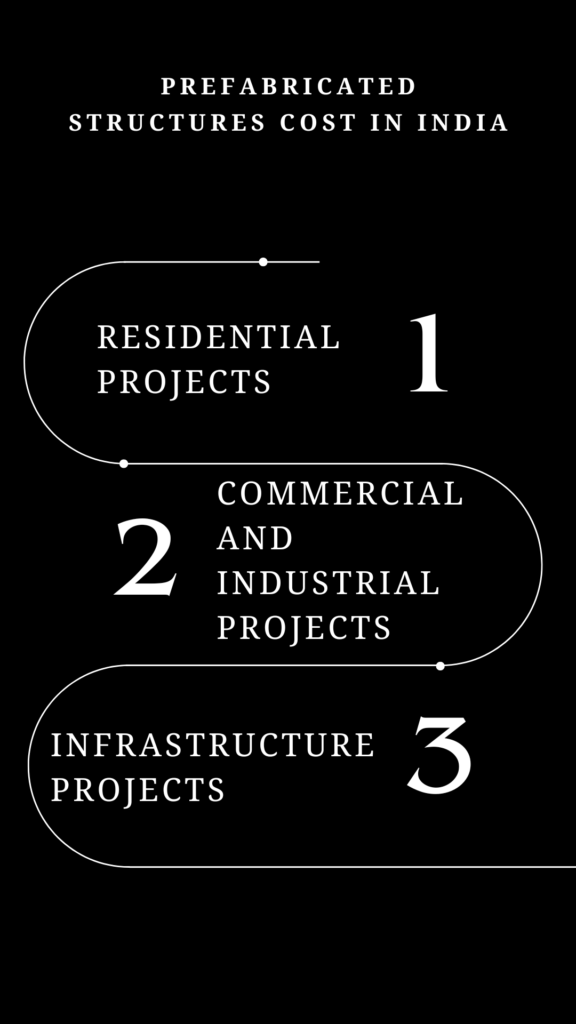
- Residential Projects: For residential projects, the cost of prefabricated construction can range from INR 1,500 to INR 2,500 per square foot, depending on the specifications and finishes. This cost is generally lower than that of traditional brick-and-mortar construction, which can range from INR 2,000 to INR 3,500 per square foot.
- Commercial and Industrial Projects: Prefabricated structures for commercial and industrial purposes, such as warehouses and factories, can cost between INR 1,200 to INR 2,000 per square foot. These costs are influenced by factors such as the complexity of the design, the quality of materials used, and the location of the project.
- Infrastructure Projects: The cost of prefabricated components for infrastructure projects, such as bridges and metro rail systems, varies widely based on the scale and complexity of the project. However, prefabrication is generally considered more cost-effective than traditional methods due to the reduced construction time and associated costs.
Challenges in Adopting Prefabricated Structures in India
Despite the numerous benefits, the adoption of prefabricated structures in India faces several challenges:

- Lack of Awareness and Education: Many stakeholders in the construction industry are still unaware of the benefits of prefabricated structures or are hesitant to adopt new methods due to a lack of understanding. Education and awareness campaigns are needed to promote the advantages of prefabrication.
- Initial Investment: While prefabrication offers long-term cost savings, the initial investment required for setting up a prefabrication facility or purchasing prefabricated components can be high. This can deter small and medium-sized developers from adopting this method.
- Skilled Workforce: Prefabrication requires a skilled workforce trained in modular construction techniques. India faces a shortage of skilled labor in this area, which can hinder the widespread adoption of prefabricated structures.
- Regulatory Hurdles: The Indian construction industry is heavily regulated, and obtaining the necessary approvals and permits for prefabricated structures can be challenging. Streamlining regulatory processes and providing incentives for prefabricated construction can help overcome this barrier.
The Role of Technology in Advancing Prefabrication
Technology plays a crucial role in advancing the use of prefabricated structures in construction. Innovations such as Building Information Modeling (BIM), 3D printing, and advanced manufacturing techniques have significantly improved the efficiency and precision of prefabricated components. These technologies enable better design coordination, reduce errors, and enhance the overall quality of prefabricated structures.
The use of technology also facilitates better communication and collaboration among project stakeholders, including architects, engineers, and contractors. This ensures that all parties are aligned and working towards a common goal, reducing the likelihood of delays and cost overruns.
Conclusion: The Future of Prefabricated Structures in India
The rise of prefabricated structures in India represents a significant shift towards more efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective construction practices. As the demand for infrastructure and housing continues to grow, prefabrication offers a viable solution to meet these needs while minimizing environmental impact and resource consumption.
With the Indian government’s support and the adoption of advanced technologies, the future of prefabricated structures in India looks promising. By addressing the challenges and leveraging the benefits of prefabrication, the construction industry can continue to innovate and deliver high-quality projects that meet the evolving needs of the Indian market.
As more developers and contractors recognize the value of prefabricated structures, we can expect to see a continued rise in their adoption across various sectors, from residential and commercial to industrial and infrastructure projects. The shift towards prefabrication is not just a trend but a transformative change that has the potential to reshape the future of construction in India.