The construction industry is synonymous with complexity, demanding significant financial investments, extensive planning, and meticulous coordination among various stakeholders. Effective financial management and cost control are pivotal to the success of any construction project. Without these, projects can face delays, budget overruns, and, in the worst cases, financial ruin. This blog explores key strategies for construction financing and cost management, offering insights into how to manage construction projects efficiently and within budget.

Understanding Construction Financing
Construction financing is the process of securing funds to cover the costs of a construction project. This involves planning, obtaining, and managing the financial resources necessary to complete a project from inception to completion. There are various sources of construction financing, including bank loans, private equity, government grants, and bonds.
Types of Construction Financing
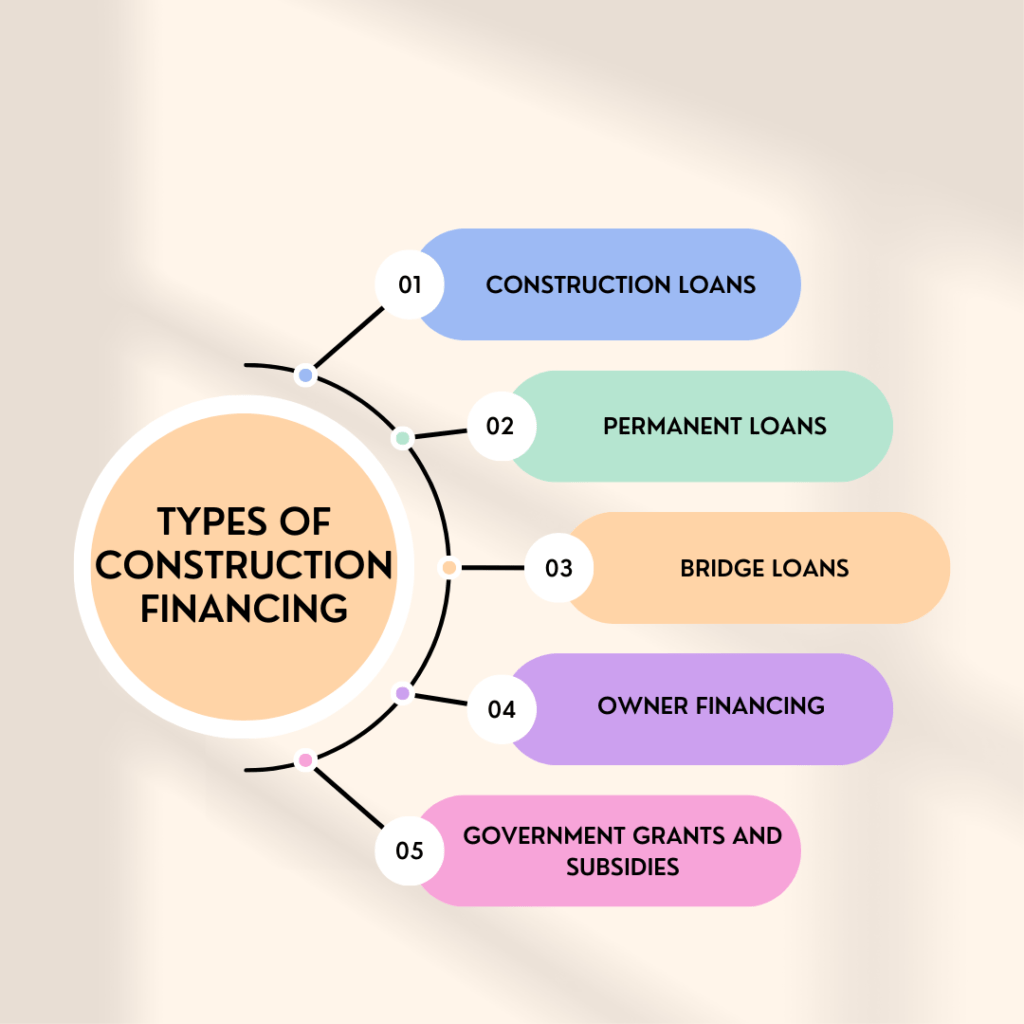
- Construction Loans: Short-term loans specifically designed to cover the cost of building a project. These loans are typically disbursed in stages as the project progresses.
- Permanent Loans: Long-term loans that take over once a construction project is completed, converting the short-term construction loan into a mortgage.
- Bridge Loans: Short-term loans that provide immediate funds to cover gaps between stages of financing.
- Owner Financing: Financing provided directly by the property owner or developer, often used when traditional financing is unavailable.
- Government Grants and Subsidies: Financial assistance from government programs aimed at promoting construction in certain sectors or regions.
Securing Construction Financing: Key Steps for Success
Securing financing for a construction project involves a series of detailed steps that ensure the project’s financial viability and smooth execution. This process includes conducting a feasibility study, developing a financial plan, preparing and submitting loan applications, and negotiating favorable loan terms. Here’s a comprehensive overview of these essential steps.
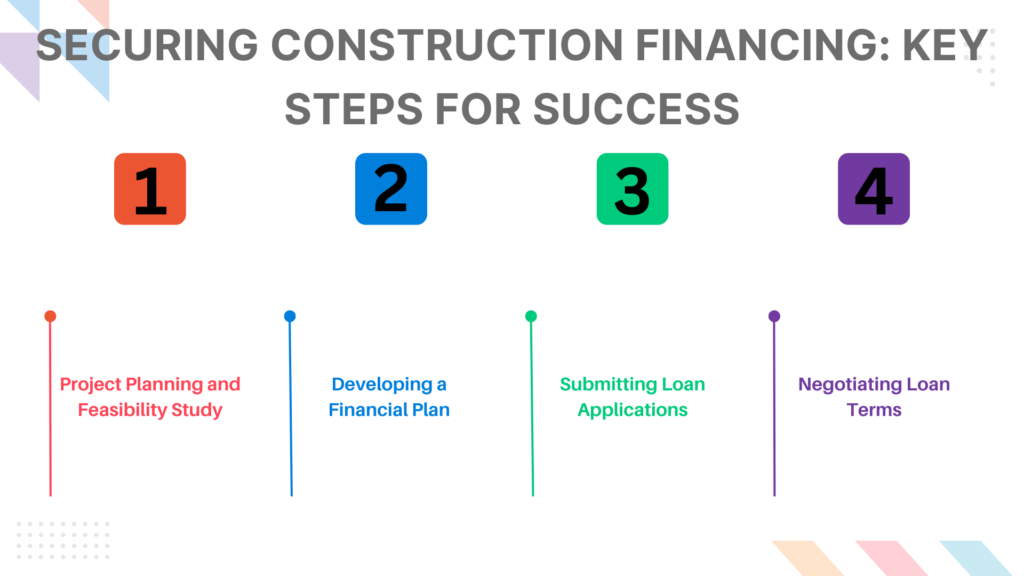
Project Planning and Feasibility Study
The initial step in securing construction financing is conducting a thorough feasibility study to assess the project’s viability. This involves several critical analyses:
- Market Analysis: Evaluate the demand for the project type in the target area. For residential projects, consider housing demand, demographics, and economic conditions. For commercial projects, assess the need for office space, retail outlets, or industrial facilities.
- Site Analysis: Determine the suitability of the proposed location by examining zoning laws, environmental impact, accessibility, and proximity to infrastructure such as roads and utilities.
- Technical Feasibility: Assess whether the project can be constructed as planned. This includes evaluating site conditions like soil quality and topography, and ensuring compliance with building codes and regulations.
- Financial Feasibility: Estimate the total project cost, including land acquisition, design, construction, permits, and other expenses. Compare this with anticipated revenues or benefits to determine financial viability.
Identifying potential risks and developing mitigation strategies is crucial. Risks could include construction delays, cost overruns, and market changes. Addressing these risks proactively helps convince lenders of the project’s robustness.
Developing a Financial Plan
A comprehensive financial plan outlines the total budget, funding sources, repayment plans, and cash flow projections:
- Total Budget: Include all projected costs, such as direct costs (materials, labor, equipment), indirect costs (administrative expenses, permits, insurance), a contingency fund for unforeseen expenses, and financing costs (interest payments, fees).
- Funding Sources: Identify potential funding sources, including bank loans, private equity, government grants and subsidies, and bonds.
- Repayment Plan: Develop a detailed repayment plan that specifies the repayment schedule, cash flow projections, and sources of repayment. This ensures that the project will generate sufficient funds to meet repayment obligations.
Submitting Loan Applications
A well-prepared loan application is essential for securing financing. It includes:
- Project Plans: Detailed architectural and engineering plans outlining the project’s scope and design.
- Cost Estimates: Accurate estimates of all project costs, prepared by a qualified cost estimator.
- Financial Statements: Historical and projected financial statements for the developer or construction company, including balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements.
- Feasibility Study: A comprehensive report demonstrating the project’s viability and addressing potential risks.
- Business Plan: An overview of the project, including objectives, target market, competitive analysis, marketing strategy, and management team.
Submitting applications to multiple financial institutions can increase the chances of securing favorable terms. Follow up with lenders to address any questions and provide additional information as needed.
Negotiating Loan Terms
Securing favorable loan terms is crucial for the project’s financial health. Key aspects to negotiate include:
- Interest Rates: Aim for the lowest possible interest rate to reduce the overall financing cost. This may involve leveraging competitive bids from different lenders.
- Repayment Schedule: Negotiate a schedule that aligns with the project’s cash flow, such as interest-only payments during construction and principal repayments once revenue is generated.
- Disbursement Conditions: Ensure the disbursement schedule aligns with project milestones, providing sufficient funds at each stage.
- Collateral and Guarantees: Minimize personal liability while providing adequate security to the lender.
Ensuring that loan agreements comply with legal and regulatory requirements is essential. Legal advisors can help review terms and protect your interests.
Cost Management in Construction
Cost management in construction is a vital process involving the careful planning, estimation, budgeting, monitoring, and control of expenses to ensure a project is completed within its financial limits. This process starts with accurate cost estimation, which considers all potential expenses, including materials, labor, equipment, and overheads, to set a realistic budget. Effective cost management also includes continuous monitoring of actual expenditures against the budget and implementing corrective measures to avoid cost overruns.
Cost control is about optimizing resources and finding cost-effective solutions without compromising quality or timelines. Techniques like value engineering can be utilized to achieve desired outcomes at the lowest possible cost. Advanced cost management often involves digital tools and software that provide real-time data for better decision-making, allowing managers to track expenses, generate reports, and forecast future costs.
In today’s competitive market, robust cost management is essential for minimizing financial risks, maximizing resource efficiency, and improving profitability. By adopting best practices and leveraging technology, construction firms can ensure project success, build trust with clients, and maintain a competitive advantage. Effective cost management not only helps achieve project goals but also supports sustainable growth in the evolving construction industry.
Key Strategies for Cost Management

- Detailed Project Planning: Comprehensive project planning is the foundation of effective cost management. This involves creating a detailed project scope, defining objectives, and developing a timeline. Detailed planning helps identify potential risks and allows for better allocation of resources .BOQ can also be considered as a crucial part of this.
- Accurate Cost Estimation: Accurate cost estimation is crucial for budgeting and financial planning. This includes direct costs (materials, labor, equipment) and indirect costs (overheads, contingency). Using historical data, industry benchmarks, and advanced estimation tools can enhance the accuracy of cost estimates.
- Budgeting: Developing a realistic budget based on accurate cost estimates is essential. The budget should include all anticipated costs and a contingency fund to cover unexpected expenses. Regularly reviewing and updating the budget as the project progresses helps maintain financial control.
- Cost Control and Monitoring: Implementing robust cost control mechanisms ensures that the project stays within budget. This involves regular monitoring of actual costs against the budget, identifying variances, and taking corrective actions. Effective cost control requires detailed record-keeping and real-time tracking of expenses.
- Procurement Management: Efficient procurement management can lead to significant cost savings. This includes selecting suppliers and subcontractors through competitive bidding, negotiating favorable terms, and managing contracts effectively. Bulk purchasing and strategic sourcing can also reduce costs.
- Risk Management: Identifying and managing risks proactively can prevent cost overruns. This involves conducting risk assessments, developing mitigation plans, and setting aside contingency funds. Regular risk reviews and updates are necessary to address emerging risks.
- Use of Technology: Leveraging technology can enhance cost management. Project management software, Building Information Modeling (BIM), and other digital tools provide real-time data, improve accuracy, and streamline processes. These tools facilitate better decision-making and cost control.
- Performance Measurement: Regularly measuring and analyzing project performance helps identify areas of improvement. Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as cost variance, schedule variance, and earned value can provide insights into the project’s financial health. Continuous performance measurement enables timely interventions and adjustments.
- Change Management: Managing changes effectively is crucial to avoiding budget overruns. This involves having a clear change management process, assessing the impact of changes on costs, and obtaining necessary approvals before implementing changes. Documenting all changes and their financial implications is essential.
- Stakeholder Communication: Maintaining transparent communication with all stakeholders ensures alignment and avoids misunderstandings. Regular updates on project progress, costs, and financial status keep stakeholders informed and engaged. Effective communication helps in managing expectations and addressing concerns promptly.
Implementing Effective Financial Management
Effective financial management goes beyond just cost control; it encompasses all aspects of managing the financial resources of a construction project. Here are some strategies for implementing effective financial management:

- Financial Planning and Forecasting: Developing a comprehensive financial plan and regularly updating financial forecasts are critical. This includes projecting cash flows, planning for capital expenditures, and anticipating financial needs. Accurate financial forecasting helps in securing necessary funds and managing cash flow effectively.
- Cash Flow Management: Managing cash flow is vital to ensuring the smooth execution of a construction project. This involves monitoring cash inflows and outflows, maintaining sufficient liquidity, and planning for peak financial requirements. Effective cash flow management prevents financial bottlenecks and ensures timely payments to suppliers and contractors.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Conducting cost-benefit analysis for major decisions ensures that the financial implications are carefully considered. This involves evaluating the costs and benefits of different options and choosing the one that provides the best financial outcome. Cost-benefit analysis helps in making informed decisions and optimizing resource allocation.
- Financial Reporting and Accountability: Regular financial reporting provides insights into the financial status of the project. This includes preparing financial statements, progress reports, and budget updates. Ensuring accountability through regular audits and reviews helps maintain financial integrity and transparency.
- Financial Risk Management: Identifying and managing financial risks is crucial to protect the project’s financial health. This involves assessing risks such as cost escalations, delays, and funding shortfalls, and developing mitigation strategies. Having insurance coverage and contingency plans in place provides additional financial security.

Conclusion
Effective financial management and cost control are essential for the success of construction projects. By implementing robust strategies for construction financing, accurate cost estimation, budgeting, and cost control, construction firms can ensure that their projects are completed on time and within budget. Leveraging technology, managing risks proactively, and maintaining transparent communication with stakeholders further enhance financial management.
In an industry where financial mismanagement can lead to significant losses, adopting best practices in financial management and cost control is not just beneficial—it is necessary. By focusing on these areas, construction firms can achieve better financial outcomes, enhance project performance, and deliver greater value to their clients and stakeholders.
In the ever-evolving landscape of construction, staying ahead in financial management and cost control will continue to be a critical factor in achieving project success and sustaining long-term growth. As the industry embraces new technologies and innovative practices, the principles of effective financial management will remain a cornerstone of successful construction project execution.